Shibarium Ecosystem Analysis
Key Insights
- Comprehensive intel on Shibarium including its blockchain overview, history, goals, comparative analysis, and architecture
- The eagerly anticipated Shibarium Ethereum layer-2 blockchain mainnet launch happened on August 16, 2023
- SHIB The Metaverse allows owners to gain passive income by way of leasing their parcels of land, for instance
What Is Shibarium
Shibarium is a blockchain platform designed to offer greater scalability and security. The core architectural feature of Shibarium lies in the combination of two key concepts: Proof of Stake (PoS) and Plasma.
Users can buy SHIB on SimpleSwap.
The Shibarium PoS approach enables rapid transaction processing, reduces fees, and ensures network security through mechanisms like staking and validator voting. Plasma technology provides security guarantees and the ability to create side chains for easier state transitions and reduced load on the main blockchain.
- History and Goals of Creating Shibarium
Shibarium blockchain platform was developed in response to the limitations faced by existing blockchain platforms like Ethereum. The founders of Shibarium recognized the need for a more efficient and accessible alternative.
The primary goal of Shibarium is to provide users and developers with a blockchain platform that offers high performance at low fees while ensuring reliability and security. The platform aims to become an perfect environment for creating dApps, games, and other projects.
- Comparative Analysis
A comparison between Shibarium and Ethereum highlights key differences between these two platforms. While Ethereum was one of the first platforms for smart contracts, it encountered issues with scalability and high fees.
Shibarium addresses these problems by employing a hybrid approach that combines PoS and Plasma. This ensures high throughput, reduced fees, and network security. Shibarium also actively works on compatibility and transitioning to future technological trends like Web 3 and Web 4.
Shibarium Architecture & Ethereum Layer
The Ethereum Layer comprises a set of smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum blockchain.
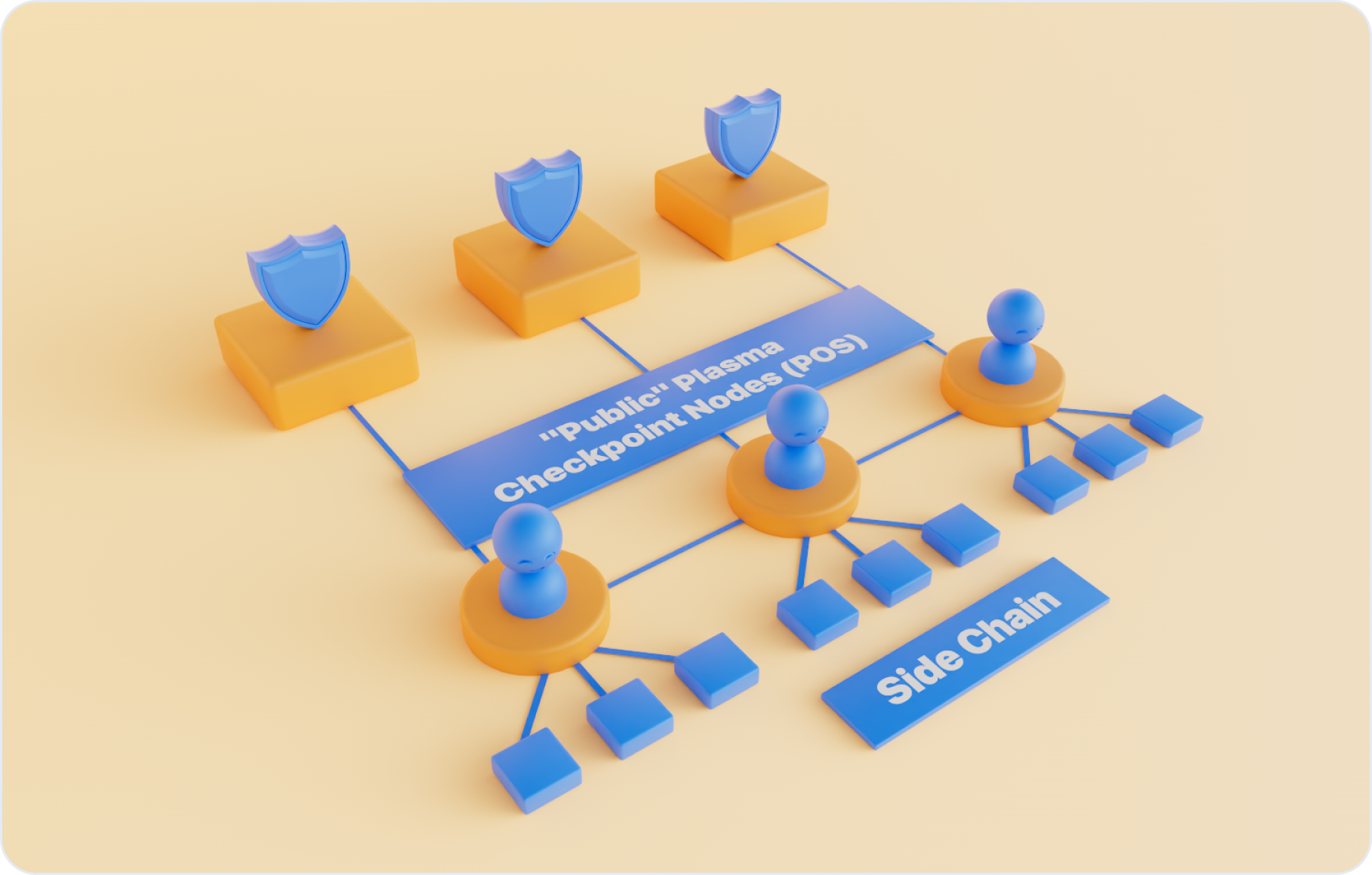
These smart contracts fulfil several crucial functions, including staking management, checkpoint preservation, penalties for malicious validator actions, and other aspects tied to the Shibarium Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism.
The architecture of Shibarium is an element that facilitates the functioning of this blockchain platform. It consists of three main components: Ethereum Layer, Heimdall Layer, and Bor Layer.
- Heimdall Layer
The Heimdall Layer consists of Proof of Stake (PoS) Heimdall nodes that collaborate with the Ethereum Main Network. The primary task of the Heimdall Layer is to establish a connection between Ethereum and the Bor Layer, as well as manage the validator and block producer selection process.
Within the Heimdall Layer, a validator rotation mechanism activates upon block completion using the EndBlocker. This layer is also responsible for creating and sending checkpoints to the Ethereum blockchain.
Key components of the Heimdall Layer include the Encoder (Pulp), used for transaction verification, and the Ante Handler, which performs transaction validation, verification, and fee collection.
- Bor Layer
The Shibarium Bor Layer is responsible for block production and is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) sidechain. Currently, the Bor Layer is based on Geth implementation with a customized consensus algorithm.
An important feature of the Bor Layer is its EVM compatibility that allows the use of apps and tools developed for Ethereum. The Bor Layer synchronizes with Heimdall to select block producers and verifiers. Block producers in this layer are formed from the validator pool based on their stakes, and periodic block producer rotation occurs.
An integral part of the Bor Layer is the Genesis Contracts, encompassing Bor validators, the BONE ERC20 token contract, and the State Receiver contract. The Bor Fee Model, where transaction fees in the network in the form of Shibarium BONE tokens are distributed among block producers.
Blockchain Scaling through Sidechains
One of the key aspects of the Shibarium architecture is the use of sidechains to achieve scalability. Sidechains allow transactions and state transitions to occur in separate parallel chains, reducing the load on the main network and increasing its performance.
The Plasma mechanism also contributes to scalability by enabling users to conduct certain types of transactions without the need to interact with the main chain.
Ethereum-Shibarium Bridge
To establish a connection between Shibarium and the Ethereum network, a bridge is employed. A bridge is a solution that facilitates the transfer of data and assets between these two networks.
The bridge enables the movement of assets and information between Ethereum and Shibarium. For instance, users can engage in the process of burning BONE tokens on Shibarium, leading to their removal from circulation and exchange for SHIB on Ethereum. This mechanism ensures interoperability between networks and enables users to perform operations in different environments.
In conclusion, the Shibarium solutions, including PoS, Plasma, and the bridge, work in conjunction to provide scalability, security, and efficient communication between different parts of the Shibarium network and the Ethereum network.
This enables the Shibarium platform to offer a high-efficiency solution for executing smart contracts and transactions within a scalable and secure environment.
Shibarium Security Models
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
This mechanism is utilized in Shibarium to ensure security and consensus. Users can lock their BONE tokens in smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain and become validators. Validators are rewarded for verifying state transitions on Shibarium and can be penalized for malicious behavior such as double-signing or downtime.
PoS also addresses data unavailability in sidechains, as checkpoints contain information about the sidechain's state, including account balances and block hashes.
This data is essential for maintaining sidechain integrity and security.
Utilized in the Shibarium network, PoS is based on validator participation, where they stake their BONE tokens to secure the network. These validators verify and confirm transactions, and their locked assets act as a guarantee of their honest behavior. PoS also addresses the data unavailability issue in sidechains.
- Plasma Security
Shibarium provides plasma assurances for various attack scenarios. Users can initiate mass exits from the plasma chain using smart contracts on the Ethereum root chain. This model ensures asset security and enhances scalability.
Users can perform specific state transitions such as exchanging ERC-20 and ERC-721 tokens and execute arbitrary transitions using Shibarium Proof of Stake functionality.
- Hybrid (Plasma + PoS)
Shibarium developers can opt for a hybrid approach, employing both Plasma Security assurances and PoS for different aspects of their DApps. For example, a gaming dApp might use PoS for securing gaming logic on the sidechain and Plasma assurances for token transactions.
dApps Creation Utilizing Shibarium Security Models
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
DApp developers can utilize PoS by deploying their smart contracts on Shibarium sidechains. This provides security and state consistency for the DApp and enables validators to receive rewards for confirming state transitions.
- Plasma Security
To create DApps with plasma assurances, Shibarium developers need to write their own predicates for their smart contracts, managing the logic of transitions from the plasma chain to the root chain. This allows DApps to use simple plasma consensus mechanisms to ensure security.
- Hybrid
Developers can combine both models in their DApps to ensure security and efficiency. For instance, a DApp can use PoS for internal state consistency and Plasma assurances for transaction processing.
Working with Plasma and PoS Assurances
Developers can utilize PoS to ensure consensus and security of their DApps' states on Shibarium sidechains. This involves validator participation and token staking in the system.
Plasma assurances are used to ensure transaction and state security and reliability on Shibarium plasma chain. This is particularly useful for projects dealing with tokens and requiring high levels of decentralization and security.
Shibarium offers developers flexibility in choosing a security model, enabling the creation of DApps with varying security and decentralization requirements.
Shibarium Token Management and Burns
Base and Priority Fees in Shibarium
The base fee represents the minimum amount of tokens a transaction must pay to be considered valid in the Shibarium network. It can vary with each block and depends on the network's load. If the previous block is close to being full, the base fee increases, and vice versa.
In Shibarium network the priority fee is the amount a transaction pays to a block producer to be included in a block. The maximum priority fee is the highest amount a transaction is willing to pay, but a block producer can accept a lower amount. The priority fee incentivizes block producers to include transactions with higher priority fees.
Token Burning Mechanism for BONE Tokens
When a user performs a transaction in the Shibarium network, the base fee is locked in the Shibarium smart contract, and the priority fee is paid to the validator.
A certain amount of BONE tokens (e.g., an equivalent of $25,000) accumulates in the burning contract. Users can initiate the burning process of BONE from Shibarium when a specific threshold is reached. At this point, the accumulated BONE tokens are sent to Ethereum Layer 1, where they are automatically exchanged for SHIB tokens.
The received SHIB tokens are burned by invoking the corresponding contract function. This process is similar to a withdrawal transaction, but instead of receiving tokens, they are burned and removed from the total supply.
Users can use a portal on the Shibarium website for this process. Anyone can initiate burning by clicking Initiate burnand complete the process by confirming several transactions for token migration.
Differences Between Base and Priority Fees
Assuming the current base fee in the Shibarium network is X BONE, and the priority fee for a specific transaction is set at Y BONE. When a validator includes this transaction in a block, they receive the priority fee of Y BONE as a reward for including the transaction in the block.
However, the base fee of X BONE is not paid to the validator. Instead, it is converted into SHIB and burned, meaning it is removed from circulation and reduces the total Shibarium coin supply. This mechanism helps prevent inflation and ensures that validators have no incentive to artificially increase the base fee to earn more rewards.
Perspectives of Shibarium After Launch
Shibarium Launch
The major Shibarium news of recent is the long anticipated Shibarium Ethereum layer-2 blockchain mainnet launch. Shibarium release date was August 16, 2023. This happened after long and meticulous testing period resulting in creation of 21 million wallets. Shibarium aims at improving scalability, since it was its main challenge. This development is expected to increase the cost-effectiveness of using Shiba Inu cryptocurrency and expand its user base.
After its recent launch, Shibarium can play the following roles in the world of blockchain technologies:
- Scalability Solution
Shibarium offers a hybrid solution that can help increase the blockchain's throughput. This is crucial to ensure fast and efficient transaction processing as the user base grows.
- Decentralization and Security
The security models of PoS and Plasma can make the network more secure and less dependent on centralized nodes. This could be a positive aspect for ensuring long-term Shibarium network stability.
- Interoperability
The ability to create bridges with other blockchains, such as Ethereum, can enhance the interoperability of the Shibarium blockchain ecosystem, facilitating the transfer of assets and data between different networks.
- DApps Development
Shibarium provides developers with an environment to create decentralized applications. Diverse security models can attract developers interested in building various types of applications.
- Tokenomics
The economic mechanisms within the BONE token's internal economy are designed to incentivize active user and network participant engagement. Token burning and staking systems can influence the available token supply and demand.
- Project Diversity
Shibarium could become a foundation for various projects, contributing to ecosystem diversity and development.
The key to success of Shibarium will be its adoption and support by the community and developers. Without active participation and trust from participants, the project might encounter challenges.
The overall perception of Shibarium as a technological solution will depend on how effectively it can address existing blockchain issues and attract developers and users.
Shiba Inu Metaverse
SHIB The Metaverse is a virtual world consisting of 100,595 parcels of land and 11 HUBS (community gathering places). Each parcel of land is akin to virtual real estate and can be acquired and customized by its owner.
Owners can create distinct virtual homes and objects, imbuing their space with unique character. They can generate passive income, possibly through leasing their Shiba Inu Metaverse parcels or other mechanisms.
SHIB The Metaverse is divided into four districts (Defense District, Growth District, Technology District, Community District), each with its unique features. Owning parcels in these districts offers varying privileges that will unfold in later stages of project development. Parcels of land also possess different rarity levels affecting their availability.
SHIB is used for naming parcels, adding images, and renting hubs. Each use of SHIB leads to its burning, which can impact its market supply and, consequently, its value.
Virtual real estate can grant access to in-game resources or advantages, and participants can earn rewards for active engagement and achievements within the Metaverse.
The Shiba Inu Metaverse offers users the opportunity to own, customize, and utilize virtual land parcels, creating unique virtual spaces and earning possibilities; SHIB plays a vital role in this ecosystem.
Summary
Based on the analysis of Shibarium and Metaverse, and their impact on the SHIB ecosystem, the following conclusions can be drawn regarding the prospects of SHIB and BONE tokens.
Shibarium represents an innovative blockchain platform amalgamating Plasma and Proof of Stake elements. This ensures network scalability and security, likely to attract developers seeking effective solutions for dApps.
The Shiba Inu Metaverse project opens captivating prospects to own and customize virtual real estate. This idea is enticing for audiences interested in metaverses and virtual reality.
The SHIB and BONE token economy encompasses multiple projects and platforms, including Shibarium and Metaverse. Token burning mechanisms for BONE and SHIB's usage in virtual worlds add value to holders of these assets.
The active token burning mechanism for SHIB and BONE can positively influence the overall supply, particularly amid growing demand. This could sustain stability and potential token value growth.
Overall, the prospects for SHIB and BONE tokens appear promising, especially considering the innovations in the Shibarium and Metaverse projects.
Users can exchange all cryptocurrencies mentioned in this article for fiat or crypto on SimpleSwap.
The information in this article is not a piece of financial advice or any other advice of any kind. The reader should be aware of the risks involved in trading cryptocurrencies and make their own informed decisions. SimpleSwap is not responsible for any losses incurred due to such risks. For details, please see our Terms of Service.


