What is Polygon: Polygon Ecosystem Review
Key Insights
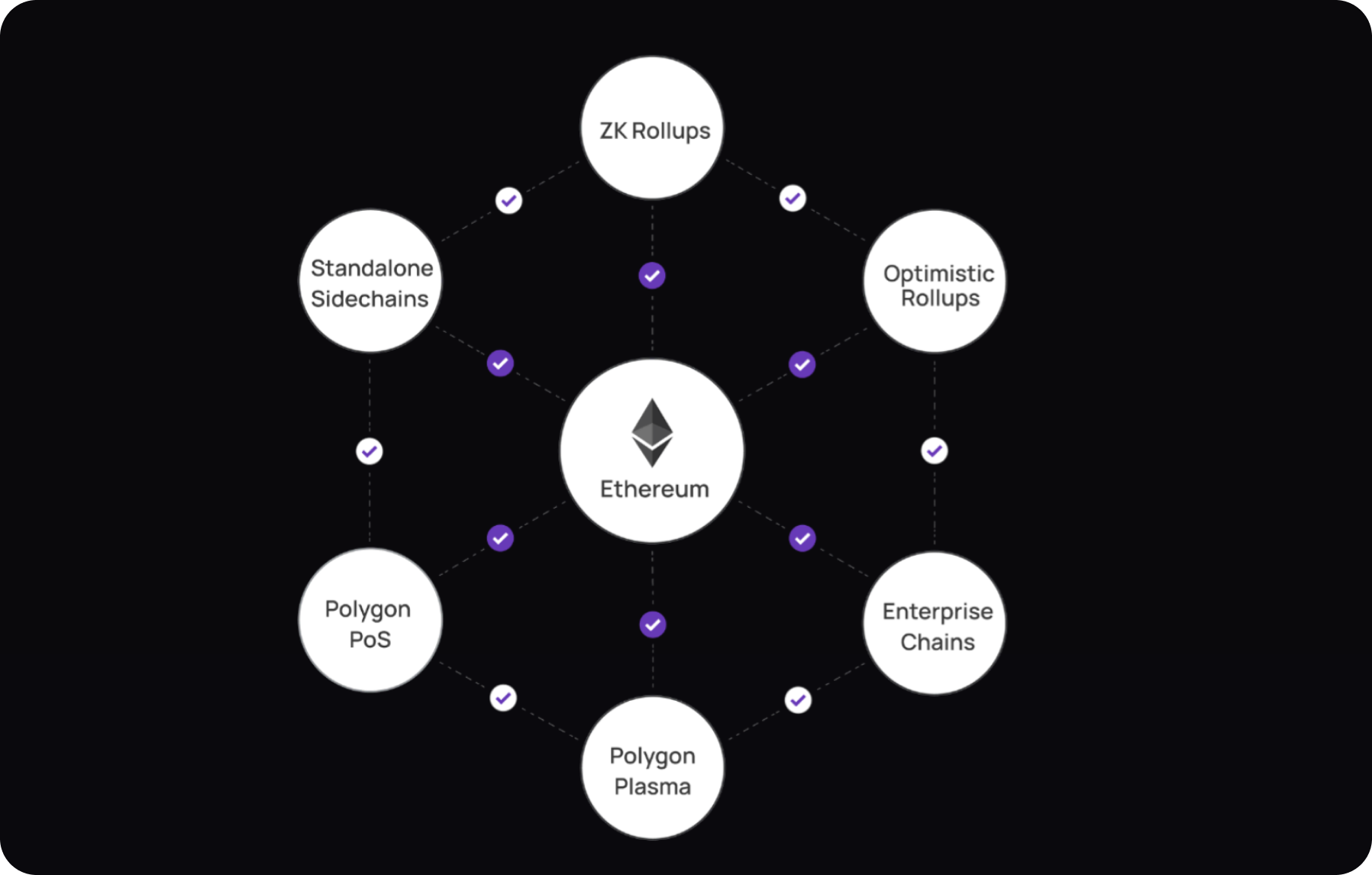
- Polygon, formerly MATIC Network, addresses Ethereum's scalability using multi-chain solutions like Plasma, ZK Rollups, and Optimistic Rollups, reducing mainnet load and fees.
- Polygon ecosystem includes sidechains like POS Matic Chain and Plasma, enabling parallel processing and scalability while ensuring interoperability through bridges.
- MATIC crypto is vital in Polygon, serving for transaction fees, staking, and Polygon ecosystem participation, bolstering platform stability and development.
Polygon is a scalable and resilient platform for building and deploying decentralized applications and blockchain services. Originally named Matic Network, the project rebranded in 2021 and became known as Polygon blockchain.
What is Polygon
The primary focus of Polygon is to enhance the performance of the Ethereum blockchain by providing multi-chain solutions and development tools.
Built on the Ethereum blockchain, Polygon offers a variety of scaling protocols and layers, such as Plasma, zk-Rollups, and Optimistic Rollups, which help reduce the load on the Ethereum mainnet and lower transaction fees.
In addition, Polygon provides tools for creating custom multi-chain applications through its development toolkit (Polygon SDK), making the platform attractive to developers. All of this enables the Polygon blockchain to build high-performance, scalable, and decentralized applications on Ethereum with minimal transaction costs.
Thus, Polygon plays a crucial role in the development of the Ethereum blockchain ecosystem.
Polygon Blockchain
The technical details of the Polygon blockchain include several key components and technologies that ensure its scalability, reliability, and functionality. Below are some of them.
Polygon Sidechain
The concept of sidechains in the context of blockchain refers to parallel blockchains that operate independently of the main chain (in this case, Ethereum) but are connected to it. Here is a more detailed explanation of how sidechains are used in the Polygon blockchain.
- Parallel transaction processing
Sidechains in Polygon are created to process transactions in parallel with the Ethereum main network. This means that transactions can be processed not only on the main network but also on sidechains, increasing the overall network throughput.
- Offloading the main chain
Using sidechains on Polygon helps reduce the load on the Ethereum main chain. Since some transactions are processed on sidechains, the main chain can focus on processing more important or critical transactions, such as large monetary transfers or changes in contract states.
- Enhanced scalability
Polygon sidechains help address the scalability issue of blockchain by distributing the workload across multiple parallel chains. This significantly increases the overall network throughput and improves its performance.
- Functionality separation
Thanks to sidechains, different types of transactions and applications can operate on separate chains, improving network efficiency and security. For example, one sidechain may specialize in processing micropayments, while another may focus on decentralized finance apps.
- Interaction with the main chain
Sidechains in Polygon are connected to the Ethereum main network through bridge mechanisms, allowing assets and data to be moved between them with minimal costs and delays. This provides interoperability between different parts of the network and expands possibilities for users and developers.
Sidechains are a key element of Polygon blockchain’s scaling technology, providing high throughput, reducing the load on the main network, and separating functionality to optimize network operation.
POS Chain
POS Chain, also known as POS Matic Chain, is the main chain in the Polygon ecosystem. This Ethereum sidechain was developed using the Proof-of-Stake (POS) consensus mechanism, which adds an additional level of security to blockchains launched on the Polygon platform.
The Proof-of-Stake (POS) consensus mechanism differs from the more common Proof-of-Work (POW) mechanism. In the POS model, network security is based on the participation of crypto holders who stake their coins to validate transactions and create new blocks.
The advantages of POS include more efficient energy usage since there's no need for computational power for proof of work, and higher network throughput.
POS Matic Chain plays a crucial role in the Polygon ecosystem, providing security and efficient operation for dApps and services running on this platform. It also serves as a foundation for deploying and testing smart contracts designed for the Ethereum network, making integration and project migration to Polygon more convenient for developers.
Polygon Plasma
The Plasma Framework is a toolkit used on the Polygon blockchain (formerly known as Matic Network), which is based on the Plasma concept, a second-layer scaling solution designed to increase the throughput of the Ethereum network.
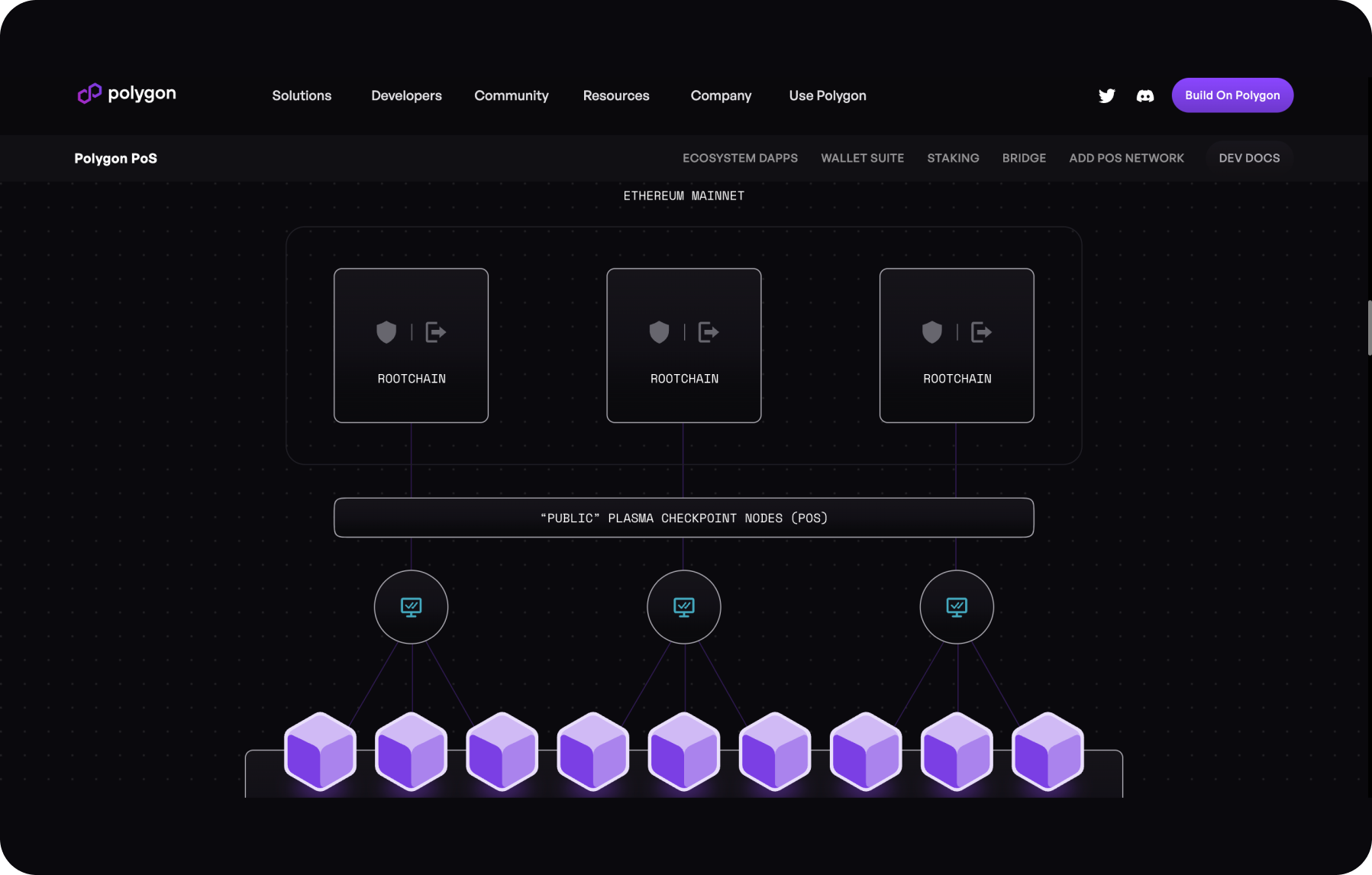
The Plasma concept offers a way to create additional side chains that operate in parallel with the main Ethereum blockchain network. Each side chain specializes in processing specific types of transactions or contracts, allowing for workload distribution and overall network performance improvement.
This scaling approach significantly increases the blockchain's throughput since each child chain can process transactions and contracts independently of other chains. Network security is ensured through mechanisms provided in the Plasma concept, such as state checkpoints and exit mechanisms.
Thus, the Plasma Framework on the Polygon blockchain plays a key role in improving the network efficiency by providing infrastructure for creating and managing side chains.
ZK Rollup
The ZK Rollup is a blockchain scaling method that allows bundling multiple transactions into one using zero-knowledge proofs. The ZK Rollup approach helps improve blockchain efficiency by reducing network load and enhancing throughput.
The core idea of ZK Rollups is to compute the result of executing multiple transactions off-chain and then present a proof verifying the correctness of this result without disclosing specific transaction data. This proof is then published on the blockchain, allowing all network participants to verify its authenticity and continue working with the new state.
Advantages of ZK Rollup
- Improved scalability
By combining multiple transactions into one, ZK Rollups significantly reduce the number of operations that need to be performed on the blockchain, thereby improving its throughput.
- Privacy preservation
Using zero-knowledge proofs helps preserve the privacy of transaction data, as they are not disclosed on the public blockchain.
- Gas savings
Since ZK Rollups reduce the number of operations needed to be executed on the blockchain, this also leads to lower transaction costs in terms of gas savings.
- Performance enhancement
By reducing network load, ZK Rollup contributes to improving blockchain performance, speeding up transaction processing, and increasing overall efficiency.
ZK Rollups represent a powerful blockchain scaling tool that helps address issues related to throughput and data privacy, while ensuring high efficiency and cost-effectiveness of operations on the blockchain.
Optimistic Rollup
Optimistic rollup is a blockchain scaling technology that operates on top of Ethereum and aims to improve its throughput. It is based on an optimistic approach to transaction verification and utilizes fraud proofs mechanisms to ensure network security.
The key principles of the Optimistic rollup are described below.
- Optimistic approach
Optimistic rollup assumes that the majority of transactions will be executed correctly and honestly. This allows reducing the network load since most operations do not require immediate verification.
- Nearly instant transactions
Thanks to the optimistic approach, transactions in Optimistic rollup can be executed almost instantly, without the need to wait for block confirmations.
- Fraud proofs
In case of disputes or suspicions of fraud, network participants can present proofs of dishonest behavior. These proofs are used to correct the network state and penalize guilty parties.
Advantages of Optimistic Rollup
- High throughput
Due to the optimistic approach to transaction verification, Optimistic rollups ensure high throughput for the Ethereum blockchain.
- Fast transactions
Transactions can be executed almost instantly, making this technology appealing to users who prioritize transaction speed.
- Low fees
Using Optimistic rollups can also reduce transaction costs due to more efficient use of network resources.
Ethereum Virtual Machine: Polygon zkEVM
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a virtual machine that executes smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. The Polygon blockchain provides compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine, hence Polygon zkEVM.
This means that developers can use existing tools, libraries, and infrastructure developed for Ethereum when building apps for Polygon. It provides significant advantages for developers, as they can utilize already proven and widely used tools and libraries available in the Ethereum ecosystem.
It also simplifies the process of migrating existing dApps from Ethereum to the Polygon blockchain or developing new apps using existing knowledge and resources.
Thanks to Polygon compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine, developers can create and maintain apps for the Polygon blockchain with minimal changes to their code. Thus, Polygon zkEVM accelerates the development of the ecosystem and expands the possibilities of blockchain technology utilization.
Polygon SDK
The Polygon SDK (Software Development Kit) is a collection of development tools that facilitate the process of creating dApps on the Polygon blockchain.
This toolkit includes various components necessary for developing and deploying apps on the Polygon blockchain.
Polygon SDK Components
- Polygon Development Tools for Smart Contracts
The SDK provides tools and libraries for writing and deploying smart contracts on the Polygon blockchain. This may include programming languages such as Solidity, as well as testing and debugging tools for contracts.
- Blockchain Interaction Interface
The Polygon SDK provides a convenient interface for interacting with the blockchain. This may include libraries for sending transactions, reading data from the blockchain, checking contract states, and other functions.
- User Interface Creation Tools
The Polygon SDK provides tools for developing a user interface for dApps. This could include libraries and tools for creating web interfaces, mobile apps, or other types of user interfaces that interact with the Polygon blockchain.
- Documentation and Guides
The Polygon SDK may come with detailed documentation, code examples, and development guides for building applications on the Polygon blockchain. This helps developers quickly familiarize themselves with using the SDK and creating their own dApps.
By using the Polygon SDK, developers can significantly accelerate the process of creating decentralized applications on the Polygon blockchain, thanks to the provision of ready-to-use tools, libraries, and documentation.
Polygon Bridge
Polygon Bridge, or Polygon bridges are mechanisms that create connections between different blockchains, allowing assets and data to be moved between these networks.
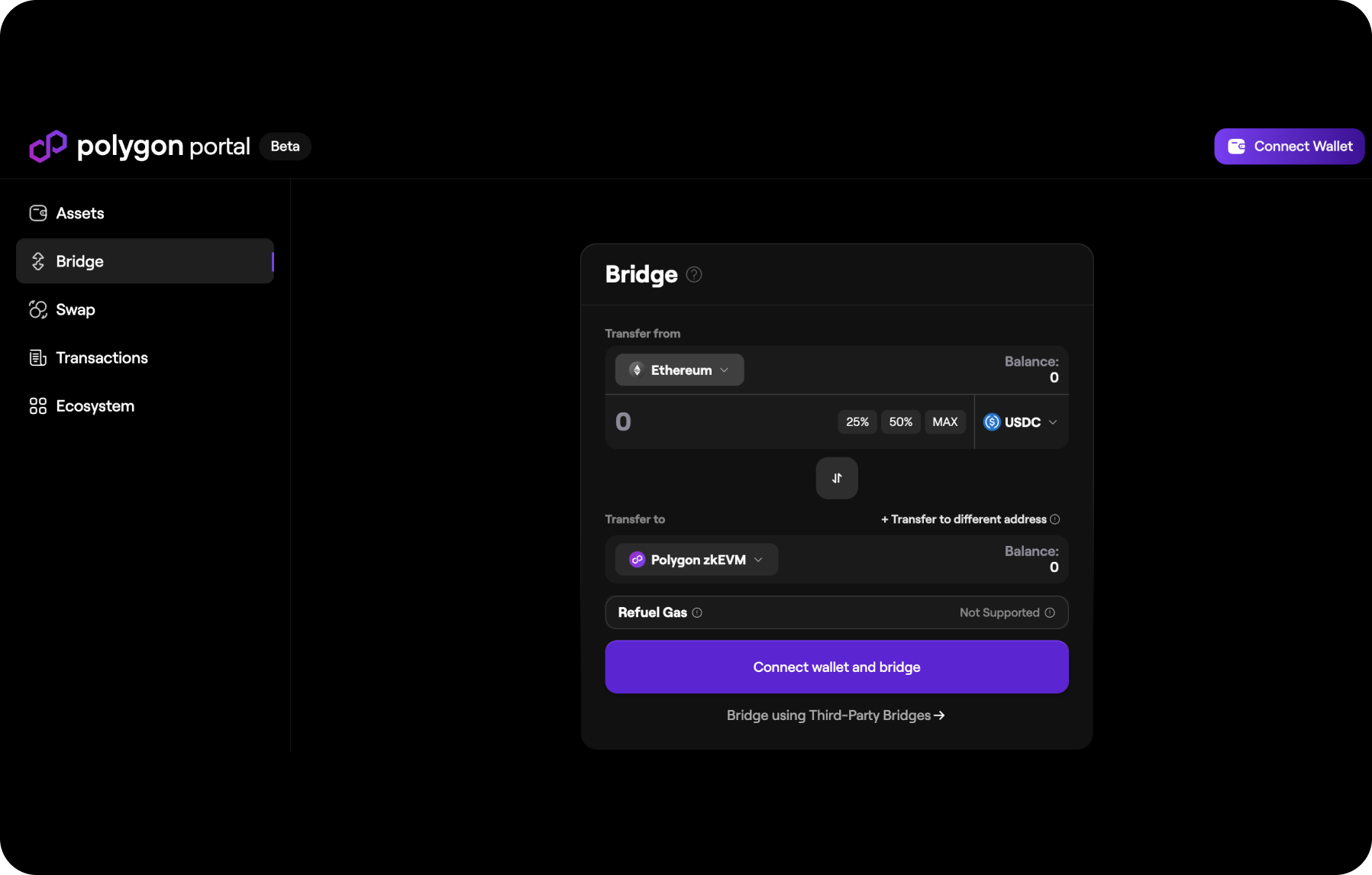
This is an important component that contributes to interoperability between different blockchains and provides users with access to diverse resources and capabilities.
Polygon Bridge Main Characteristics
- Asset Transfer
Polygon Bridges enable the movement of various tokens and other digital assets between different blockchains. For example, they can facilitate token transfers from Ethereum to the Polygon blockchain and vice versa.
- Data Transmission
In addition to asset transfers, bridges can also support the transfer of data between blockchains. This can be useful for transmitting data about transactions, the state of smart contracts, and other data between networks.
- Interoperability
Polygon bridges provide interoperability between different blockchains, allowing users to utilize assets and applications operating on different networks without the need for conversion or complex procedures.
- Decentralization and Security
Good bridges are typically based on decentralized principles and ensure secure movement of assets and data between networks. This includes security mechanisms such as multi-signature, risk management, and network governance mechanisms.
- Ecosystem Development
The presence of bridges contributes to the growth of the ecosystem by allowing projects and users to utilize various blockchains and resources for their needs.
Overall, bridges play a crucial role in the Polygon ecosystem by providing connectivity and interoperability between different blockchains.
Polygon Crypto: MATIC Polygon
The Polygon crypto, usually denoted as MATIC, is a cryptocurrency utilized within the Polygon network ecosystem. Users can get MATIC for crypto or fiat on SimpleSwap.
Below are some basic characteristics of the MATIC coin.
- Transaction Fee Payment
Users of the Polygon network use the MATIC coin to pay fees for conducting transactions and performing operations within the network. This includes token transfers, interacting with DApps, staking, and other operations.
- Staking and Voting
MATIC crypto holders have the opportunity for staking, which involves locking their MATIC for a certain period to support network security and receive rewards. They can also participate in Polygon network governance voting.
- Rewards and Incentives
In some cases, users can receive MATIC coin rewards for participating in various activities on the network, such as providing liquidity, participating in DeFi protocols, and more.
- Ecosystem Participation
MATIC also serves as a key element of the Polygon ecosystem, helping to provide economic incentives and network governance.
The MATIC crypto is a crucial component of the Polygon ecosystem and plays a role in ensuring its stability, security, and development. Read more about MATIC Polygon technical analysis including the MATIC price prediction here.
Summary
Polygon, formerly known as MATIC Network, is a scalable platform built on Ethereum that aims to improve its performance and functionality. It offers multi-chain solutions and development tools such as Plasma, ZK Rollups, and Optimistic Rollups to reduce Ethereum's mainnet load and transaction fees.
The Polygon SDK facilitates dApp creation, while Polygon bridges provide interoperability between different blockchains. MATIC coin, the Polygon crypto, is integral to the network's operations, serving as a means of payment, staking, and ecosystem participation.
In the race to be the first fully implemented solution for interoperability, Polygon strives to remain at the forefront of innovation.
The information in this article is not a piece of financial advice or any other advice of any kind. The reader should be aware of the risks involved in trading cryptocurrencies and make their own informed decisions. SimpleSwap is not responsible for any losses incurred due to such risks. For details, please see our Terms of Service.


