The Role of Sidechains in Blockchain Scalability
This blog post will cover:
- Understanding Sidechains
- Their Role in Blockchain
- How Do Sidechains Work?
- Security Aspects
- Challenges of Integrating Sidechains
- The Future of Scalability
Think of blockchain as a crowded library where everyone is trying to check out books at the same time, causing long delays. Now, imagine special side rooms where people can borrow and return books without waiting. Sidechains can be thought of as such rooms in the blockchain world. Ready to explore how sidechains work, and how they can take the efficiency of online transactions to the next level? Let's dive in.
Understanding Sidechains
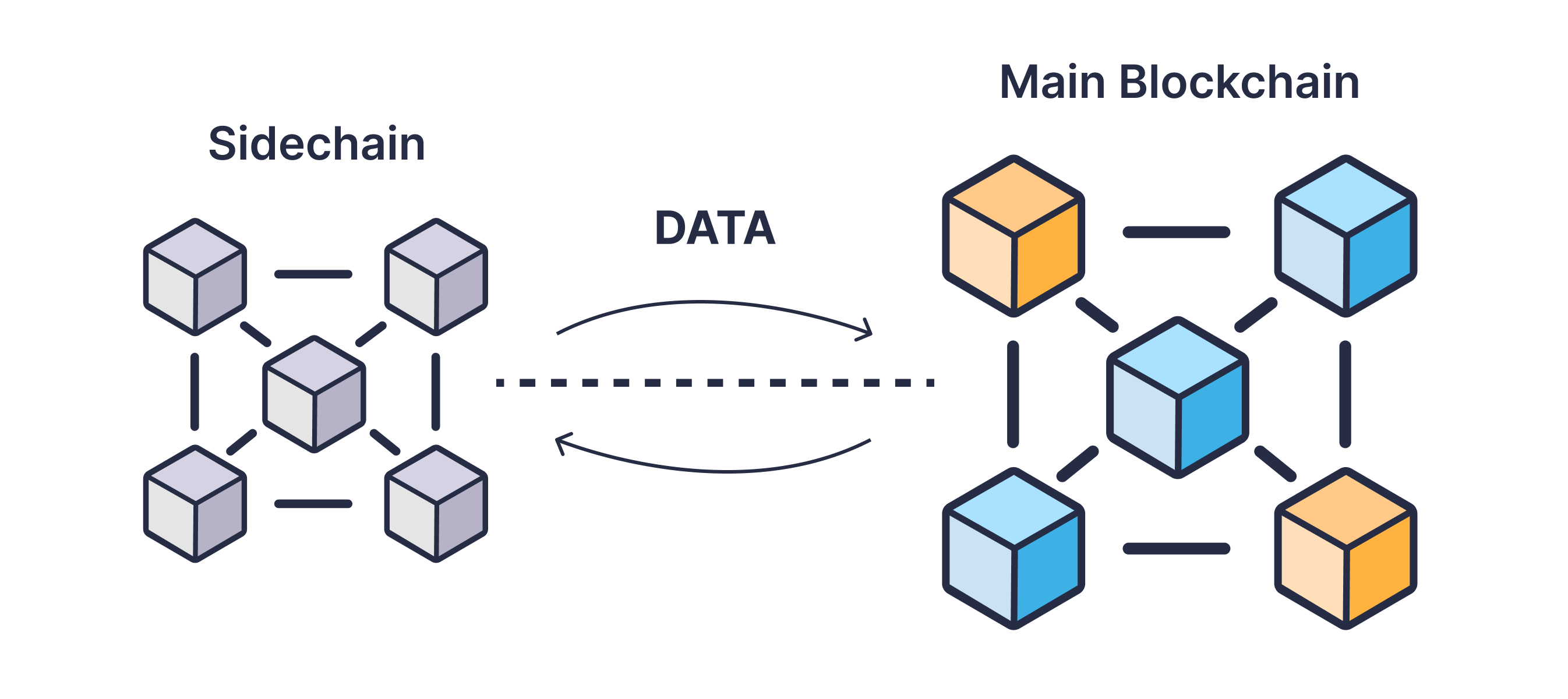
Sidechains, as the term suggests, operate parallel to the main blockchain. They improve blockchain scalability by handling transactions separately from the main chain. This reduces the load on the primary blockchain, enhancing its efficiency and speeding up transaction processing.
When answering the question of what are sidechains in blockchain, one needs to distinguish between three main types: federated, SPV Proved, and drivechain, each offering distinct features and capabilities.
Federated: these are overseen by a predetermined cluster of nodes, referred to as a federation, managing asset transfers between the primary blockchain and the sidechain. They prove advantageous in scenarios necessitating transaction confidentiality within a specific group.
SPV Proved: they use Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) proofs to handle the transfer of data from the main blockchain to the sidechain. This verification proof comprises the block header containing the SPV-locked output, a series of linked block headers, the transaction that includes the output, the specific index of the output within the transaction, and a merkle path that authenticates the transaction's inclusion in the block.
Drivechains: here, miners participate in voting on the sidechain's status. Drivechains facilitate the establishment of sidechains enabling experimentation with novel features and functionalities while safeguarding the main chain's security and integrity. They offer advantages such as unrestricted experimentation, the introduction of new features or application scenarios, the mitigation of competition among blockchains, and improved scalability.
Their Role in Blockchain
Blockchain networks, especially those working with PoW, commonly encounter issues related to scalability. The primary concern revolves around their restricted ability to process transactions per second, resulting in delays and increased expenses, which can impede the widespread acceptance of blockchain technology.
Scalability challenges are exacerbated during periods of heightened network activity, leading to notable delays in transactions and a surge in transaction fees. This presents considerable hurdles, especially for applications that demand swift and frequent transaction execution.
Sidechain crypto offers a remedy by executing transactions on separate, parallel chains. This approach eases the burden on the main chain, resulting in faster transactions and lower costs. Consequently, even during peak network congestion, this concept is what ensures prompt and efficient transaction processing.
How Do Sidechains Work?
Transferring assets between the main blockchain and a sidechain depends on a system called a "two-way peg." This process is vital for the functioning of sidechains and involves two primary actions: "locking" and "releasing" assets.
At the outset, when assets transition from the primary blockchain to a sidechain, they undergo a process known as "locking" on the primary chain. This step essentially withdraws them from circulation on the primary chain, essentially "freezing" them to prevent concurrent spending on both chains, thereby averting double-spending.
Following this, an equal amount of assets is "unlocked" on the sidechain, permitting their utilization within the sidechain as regular assets. To transition assets back to the main chain, the procedure is inverted: assets on the sidechain are "locked," and the corresponding assets on the main chain are "unlocked," becoming available for use once more. This guarantees a consistent total asset count, regardless of their distribution between the chains.
How do sidechains affect transaction speed and fees?
This technology has the potential to greatly enhance the speed of financial operations and lower fees within a blockchain network.
Transaction Speed
The transaction processing capacity of major networks (Bitcoin sidechains, ETH) is restricted by the limitations imposed by their consensus mechanisms. This restriction often results in delays in processing transactions, especially during periods of high network activity.
Sidechains offer a remedy by handling transactions on separate, parallel chains. By adopting this approach, they ease the strain on the main chain, thus enhancing its transaction speed.
Transaction Fees
During periods of congestion on the main blockchain, transaction fees often skyrocket. These fees act as motivators for miners to incorporate transactions into their mined blocks. Nonetheless, sidechains offer an alternative route by handling transactions off the main chain, potentially leading to decreased fees. This adaptability stems from the ability to implement diverse consensus mechanisms or fee models. For instance, a sidechain may prioritize processing numerous microtransactions with minimal fees.
Security Aspects
Sidechains might not share the same level of security, making them more susceptible to attacks.
Their security primarily relies on the selected consensus mechanism and the makeup of their network participants. Encouraging a satisfactory number of validators to participate can prove challenging, particularly for chains lacking native tokens to motivate involvement. Given their smaller scale, these chains inherently face increased susceptibility to potential security threats.
To kickstart the transfer of assets between the primary blockchain and a sidechain, users need to first safeguard their assets on the primary blockchain and generate corresponding tokens on the sidechain. Once transactions are carried out on the sidechain, users can nullify the tokens and unlock the assets for future utilization on the primary blockchain. Typically, this process is overseen by smart contracts or similar protocols to guarantee the security and trackability of assets.
As such, although sidechains offer considerable benefits in terms of scalability and functionality, they also bring forth fresh security complexities. It is imperative to grasp these potential risks and the tactics to alleviate them when contemplating the integration of the technology.
Challenges of Integrating Sidechains
Sidechains presents several drawbacks:
Decentralization trade-offs: improving throughput frequently means losing out on some degree of decentralization. Such compromise emerges because sidechains may rely on fewer validators or nodes, which could result in centralized control and undermine the decentralized nature of blockchain networks.
Complexity: establishing or sustaining demands considerable dedication and efforts. The initial configuration and ongoing management pose notable challenges, as comprehending the intricacies of sidechains and integrating them within the main ecosystem presents a multifaceted endeavor.
Interoperability and UX: challenges related to interoperability and user experience arise when creating sidechains for Ethereum. These obstacles involve addressing significant technical challenges such as maintaining security and data integrity across various chains, as well as improving interoperability and user interface.
Consensus mechanisms: these present a notable challenge in sidechain governance, especially when dealing with differing mechanisms from the main blockchain. Achieving consensus demands careful attention to uphold both security and operational efficiency.
These challenges underscore the essential need for detailed planning, robust design frameworks, and extensive testing when integrating sidechains within blockchain networks. Despite these hurdles, sidechains possess significant potential to enhance the scalability and functionality of blockchain systems, presenting a hopeful outlook for the continued progress of blockchain technology.
The Future of Scalability
Looking ahead, the importance of sidechains for enhancing scalability is becoming more obvious. With an ongoing evolution, we expect the development of stronger and more efficient sidechain protocols. These innovations will boost the performance of current blockchain platforms and enable the creation of new ones that can manage larger transaction volumes more effectively.
Moreover, as awareness and acceptance of sidechain technology grow, we can anticipate broader integration into various ecosystems. This widespread adoption will significantly alleviate the scalability challenges that have historically impeded blockchain advancement. The future of the subject in question holds great promise, potentially transforming the way we leverage blockchain technology.
In summary, sidechains are pivotal in enhancing blockchain scalability by distributing transactions across independent chains, thus optimizing the main chain's performance. Although they bring about new security concerns, these challenges are addressed through diverse strategies. As blockchain technology progresses, the significance of this tool is poised to grow significantly.
SimpleSwap reminds you that this article is provided for informational purposes only and does not provide investment advice. All purchases and cryptocurrency investments are your own responsibility.