Bonding Curves in DeFi Explained

This blog post will cover:
- Bonding Curves Explained
- Types of Bonding Curves
- Usage in DeFi
- Use case: Curve Finance
- Risks and Challenges
- Conclusion
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a highly technological sphere that took on concepts from many other spheres. Bonding curves originally came from mathematics, but now they play a big role in lots of applications. These include stablecoins, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and many other components of the Crypto World.
Today, we are having a look at the principles of work of bonding curves, their types, and the associated risks.
Bonding Curves Explained
Essentially, a bonding curve is a mathematical graph that defines how the price and supply of a token are related. It determines the fluctuations in the coin’s price as the supply goes up and down.
Thus, bonding curves create a dynamic pricing mechanism for cryptocurrencies, which makes sure that their prices are not determined by just market demand but also by a predefined formula. This helps to make a more controlled environment which is vital in the volatile crypto market.
Types of Bonding Curves
Depending on the project’s unique characteristics and use cases, bonding curves utilized in them can look different.
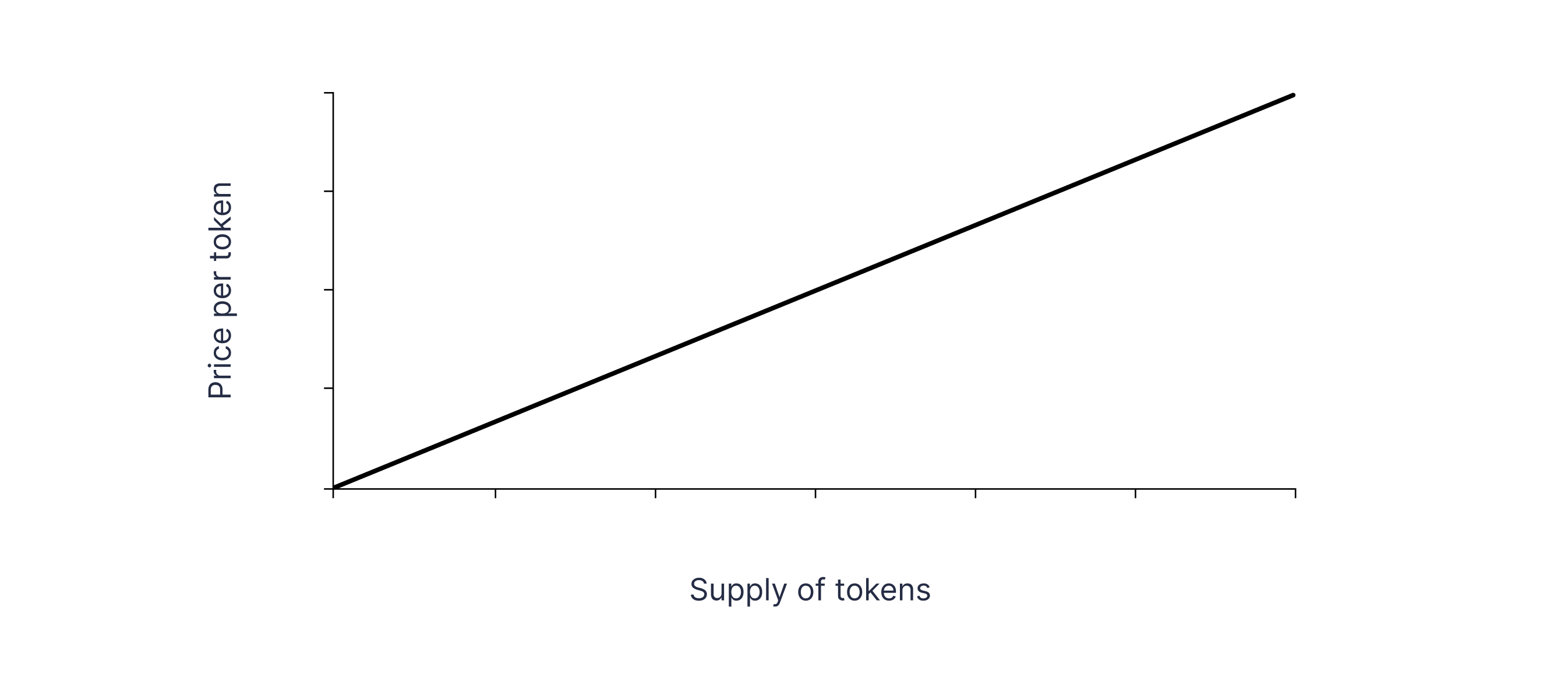
Linear. The price grows together with the supply in a straightforward way. Each new token that gets issued (or minted) increases the price by a predetermined amount. It is vital to remember that unpredictable changes may cause sharp price swings.
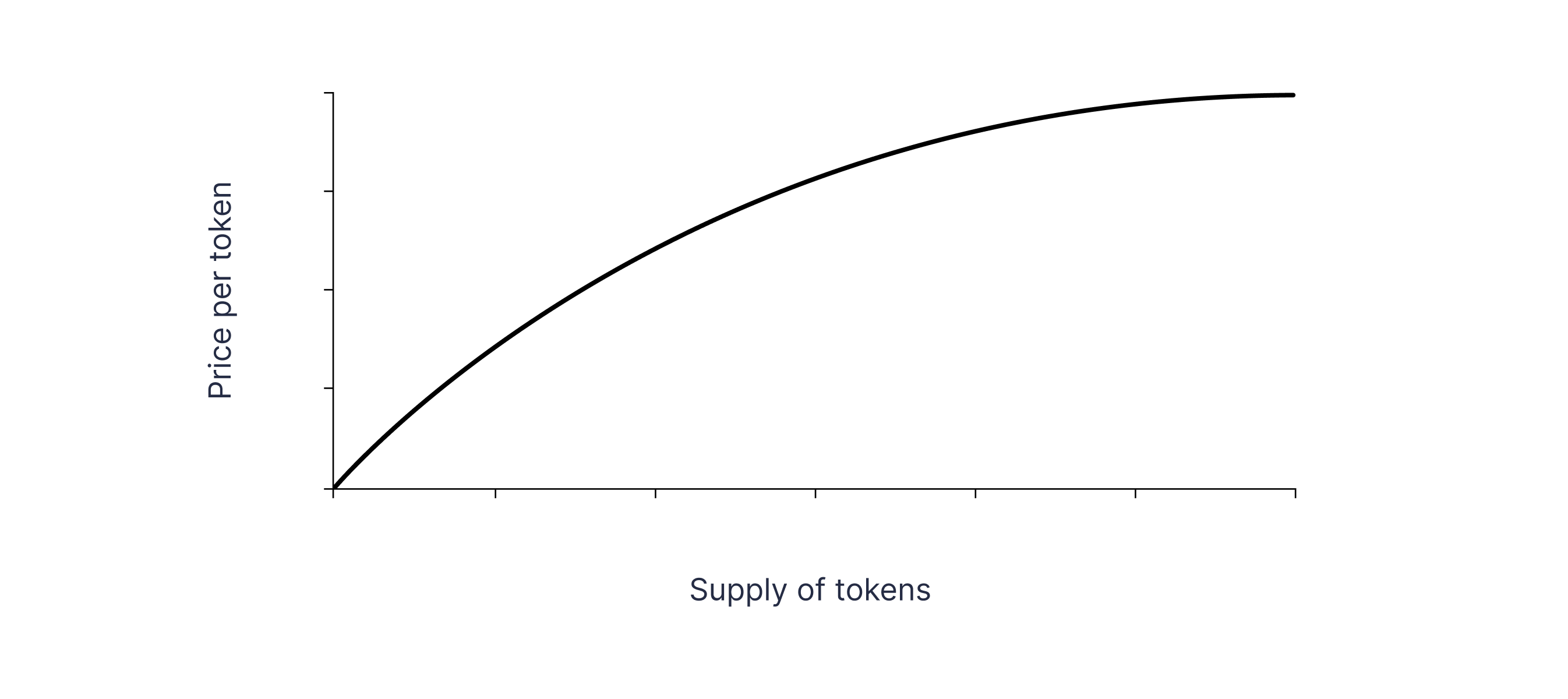
Logarithmic. As the supply grows, these curves cause the price to rise at a slower rate. To prevent token prices from rapidly becoming prohibitively expensive, this kind of curve can be utilized.
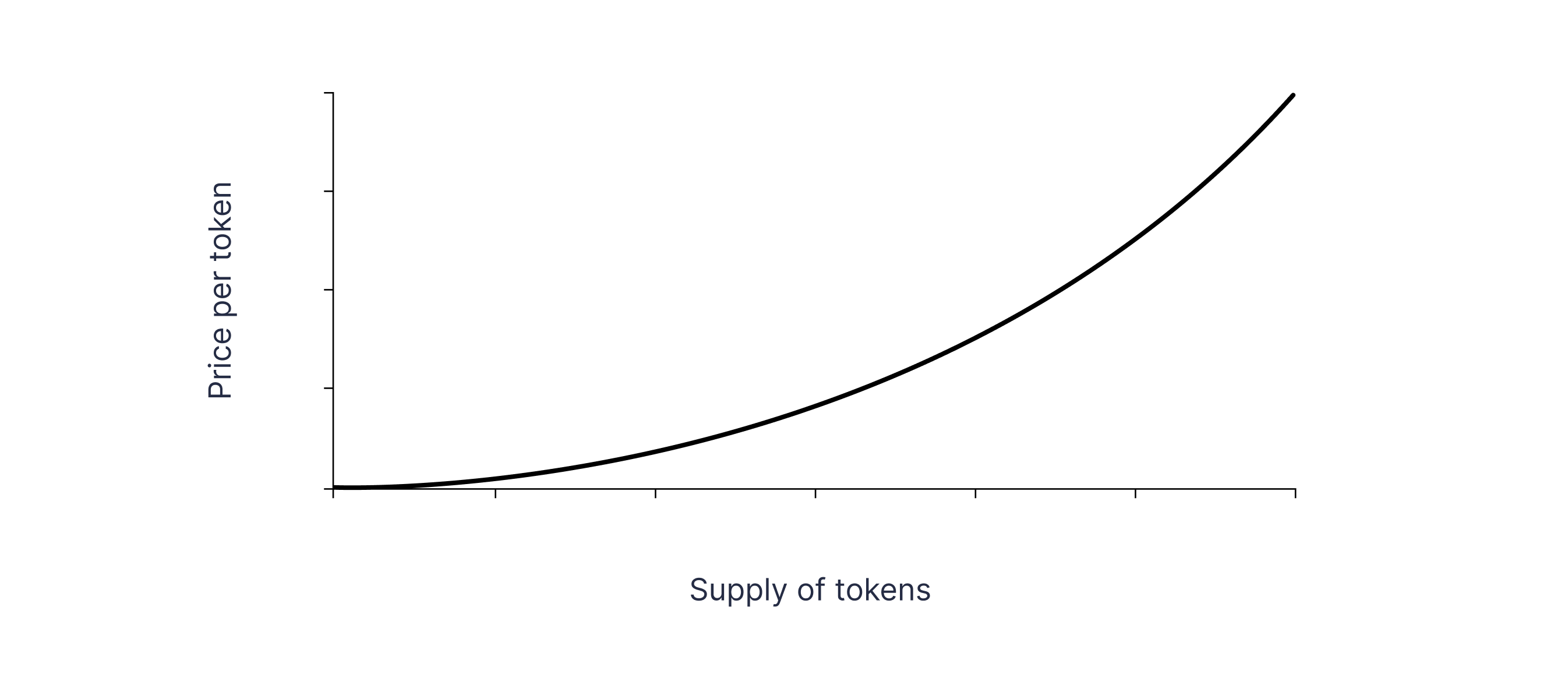
Exponential. Exponential curves are often utilized to create scarcity and stimulate early adoption, because the crypto prices rise quickly with each new issued token.
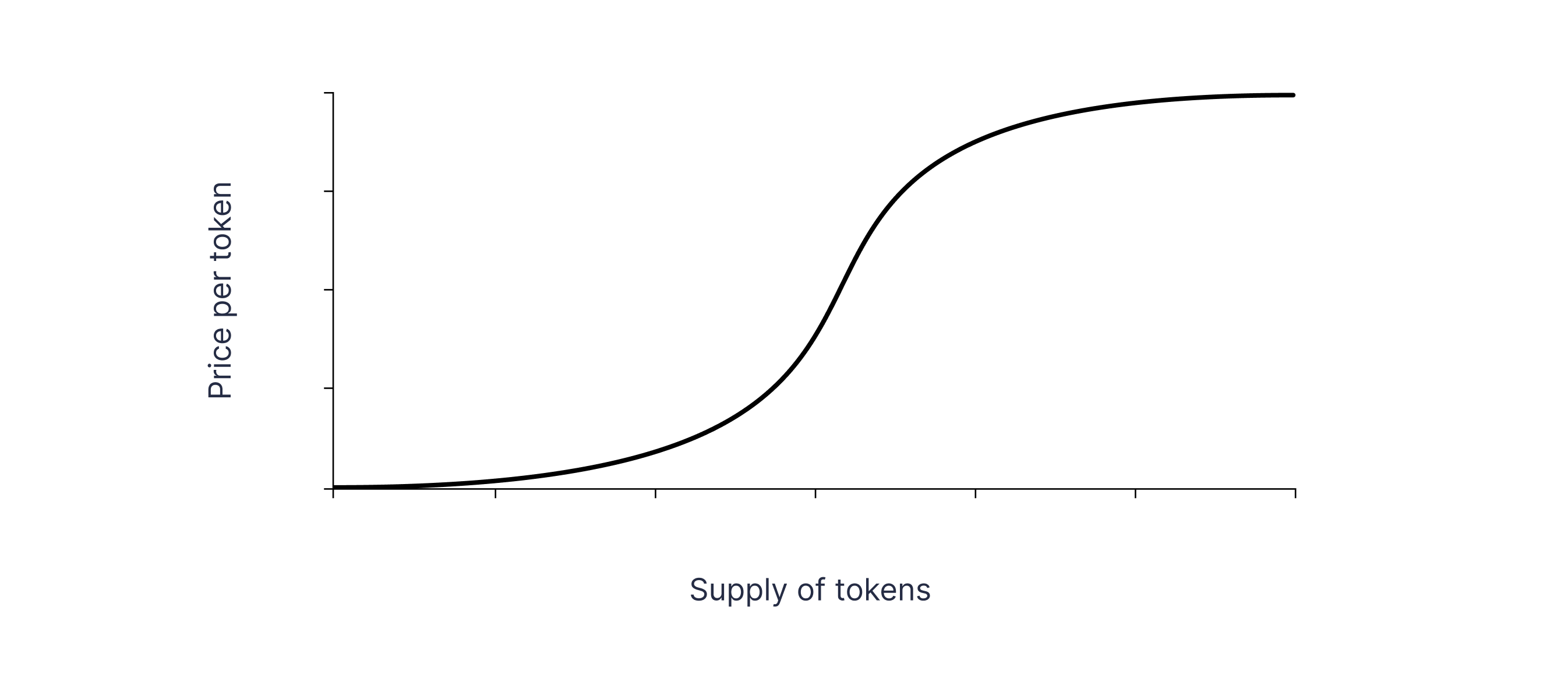
Sigmoid. These are also called S-curves, and they are exponential and logarithmic curves combined. When there is growth in supply, the price rises slowly in the start, then quickly, and then slowly again. This method is suitable for finding a balance between long-term stability and early incentives.
Usage in DeFi
Let’s see what practical applications there are for bonding curves within DeFi.
Stablecoins. These cryptocurrencies (USDT, USDC, etc.) aim to maintain a constant value in comparison to a fiat currency, gold or other assets. Bonding curves, for example, are used by some stablecoins to control collateral and maintain price stability. By adjusting the supply of tokens based on market demand, bonding curves help keep the stablecoin's value close to its peg.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). Bonding curves are used to make token issuance and governance in DAOs easier. They allow members to purchase governance tokens, ensuring that early participants acquire them at a lower cost than later participants. This system establishes a fair distribution of governance power.
Yield farming and liquidity mining. Some crypto projects use bonding curves to distribute rewards to liquidity providers, which straightens incentives and promotes more participation. The bond curve makes sure that rewards are proportional to how much liquidity is provided, which helps the liquidity pool grow over time.
DEXs. Projects like Uniswap and Curve Finance heavily feature the concept. Their automated market makers establish token prices based on supply and demand. We will consider this example in the next section.
Use case: Curve Finance
Curve Finance is a DEX optimized for the trading of stablecoins. The project uses a unique bonding curve model designed to keep the slippage minimal. Unlike traditional constant product curves, Curve employs a constant sum-like bonding curve, which is well-suited for assets with stable value relationships. This model uses an amplification coefficient to adjust how steep the curve is, simulating higher liquidity and providing efficient trading with low slippage.
Curve’s formula is necessary so that the sum of the token amounts stays close to a constant, optimizing trades between stablecoins. This is especially effective for stablecoin pools.
Low slippage and efficient liquidity use makes Curve Finance attractive for stablecoin traders and liquidity providers. At the same time, the complexity of using the amplification coefficient can be harder to understand and is specialized for stable assets.
Risks and Challenges
Even though bonding curves as a concept are widely accepted within the crypto community, there are still a few concerns that we have to take into consideration with them.
Volatility. Price volatility can be significant with bonding curves, especially when exponential curves are used. Prices can rapidly fluctuate as a result of sudden changes in supply, affecting token holders in a negative way.
Difficulty. The design and implementation of the bonding curves can be challenging. It needs an excellent comprehension of crypto market dynamics and mathematical principles. Cost inefficiencies and unintended results can come with poorly designed curves.
Liquidity risks. When the liquidity is low, bond curves can make volatility and price slippage worse. Bond curve systems can only function properly if there is sufficient liquidity.
Smart contract risks. Bonding curves, like all DeFi protocols, can be severely affected by smart contract vulnerabilities and exploits. Strict auditing and security measures are a must in mitigating these risks.
Conclusion
Bonding curves are a powerful tool in the crypto sphere, offering innovative solutions for minting tokens, pricing, and liquidity control. Their applications in DAOs, DEXs, etc. underscore their versatility and importance. However, like any technology, bonding curves come with their own set of risks and challenges. Going forward, understanding and the correct usage of this concept is likely to become key to building sustainable decentralized financial systems.
SimpleSwap reminds you that this article is provided for informational purposes only and does not provide investment advice. All purchases and cryptocurrency investments are your own responsibility.