Web3 Appchains Explained

This blog post will cover:
- What is an application-specific blockchain and how does it work?
- Appchain architecture
- Why use appchains?
- Appchain example: Cosmos
- The final word
As Web3 evolves, more users are onboarded to its new paradigm. As more users adopt Web3 technologies, the worse its performance degrades, and the higher its transaction fees rise. Therein lies its paradox.
It doesn’t pick and choose newbies and seasoned users, either. There are countless horror stories of users having to pay far out the ass in exorbitant transaction fees that may fail at any time during a highly-anticipated NFT drop. The same can happen when using a decentralized exchange at the height of a bull run.
Fortunately, application-specific chains — or appchains — have emerged as the solution to these problems inherent in Web3. With appchains, users no longer need to rely solely on a public blockchain as the base layer to run decentralized apps—and they may hold the key to the next wave of Web3 adoption. Let’s take a closer look at these chains.
What is an application-specific blockchain and how does it work?
In essence, appchains are blockchains dedicated solely to running a single application, as opposed to a public blockchain designed to run multiple apps simultaneously.
Appchains are built over existing Layer-1 distributed ledgers, improving their structure to give Web3 developers greater freedom over their apps’ governance, consensus mechanism, and economic infrastructure for maximum customizability.
Appchains also offer significantly improved performance and developer ownership, with stakeholders freely able to update, roll back, and make changes to it as necessary. Since no other apps compete for computing throughput and storage on appchains, the dedicated apps they serve run at optimal levels.
Appchains primarily use their own crypto to stake with validators or to represent ownership within an application. Application-specific crypto tokens may be used as a method of value transfer, a token of ownership, or as a governance token altogether. Since appchains use their own tokens, they do not compete with other apps on the L1 blockchain for computing capacity.
Appchain architecture
Appchains are modular systems featuring decoupled architectures that offer a wide array of benefits. Appchain architecture can be divided into five layers as follows:
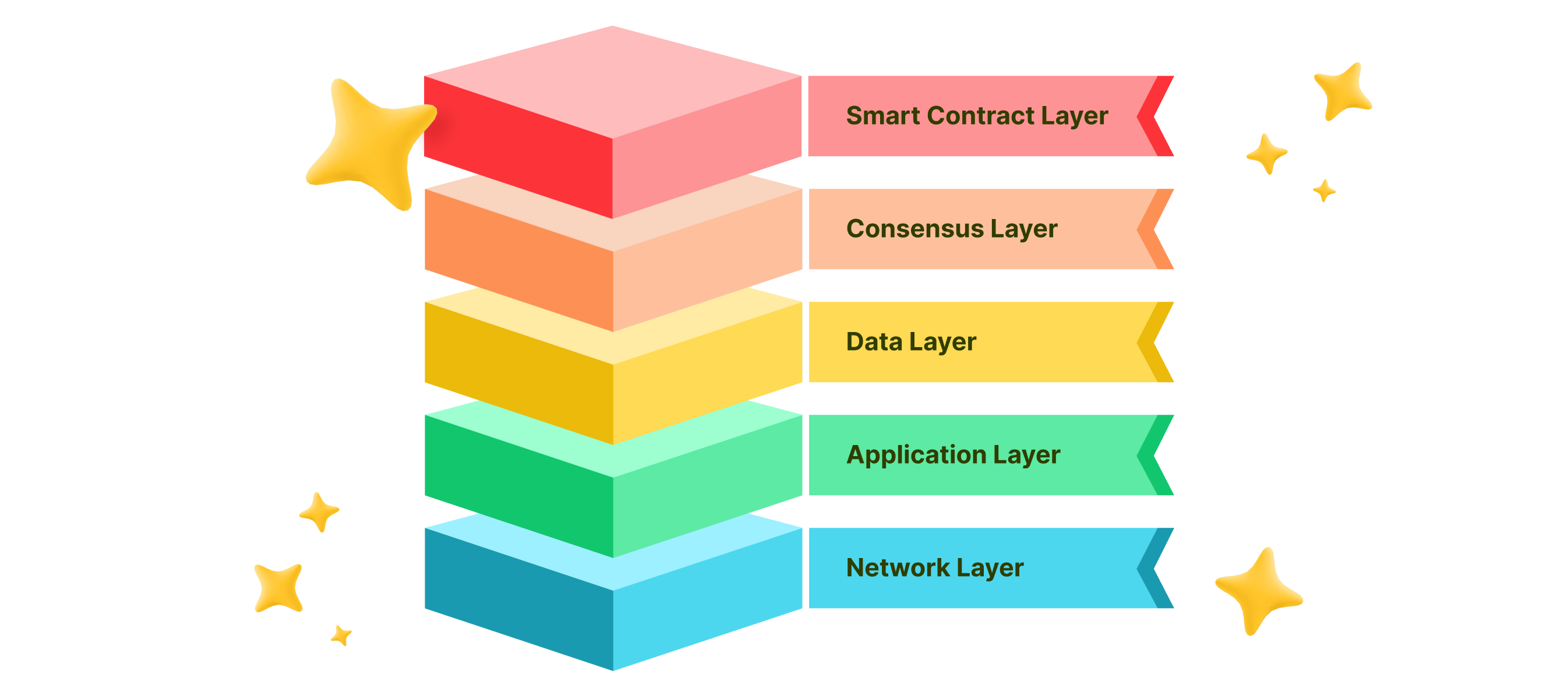
- Network Layer. This layer handles the communication between networking components to ensure successful and secure transactions between nodes within a peer-to-peer (P2P) network.
- Application Layer. This layer serves as a user interface to interact with the appchain using Web3 libraries, software development kits, or APIs, as well as giving users access to data stored within its Data Layer.
- Data Layer. This layer is responsible for storing, indexing, and organizing information in databases and other storage solutions.
- Consensus Layer. This layer determines how appchain users will agree on the appchain’s state, using consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-stake (PoS) or proof-of-work (PoW), among others.
- Smart Contract Layer. Finally, this layer determines and runs smart contract and business logic for the application supported by the appchain.
Why use appchains?
Appchains are revolutionizing the way we interact with and use distributed ledger technologies, bringing the following benefits to the table:
- Greater scalability. Layer-1 blockchains are prone to congestion and high transaction fees. Appchains, meanwhile, are more scalable so they can support greater transaction volumes and process them faster and more efficiently regardless of the number of users.
- Lower transaction costs. Appchains are significantly more affordable to use than relying on L1 blockchains. This makes transactions more flexible and convenient for users.
- Greater customizability. Appchains boast a greater level of functionality to perform secure Web3 transactions by building individual application-specific chains to support different activities. This broadens their potential to disrupt industries with their customizability.
- Improved security. Since appchains manage data on different dedicated chains, they protect data integrity and add an extra layer of security from would-be threat actors.
- Enhanced privacy. Appchains operate on private blockchains that keep transactions obfuscated from the rest of the blockchain on top of which they are built on. This keeps potentially sensitive data secure, promoting greater user privacy and data ownership in the process.
Ultimately, appchains offer a wide array of advantages over public Layer-1 blockchains, making them an optimal choice to build robust applications on private, customized networks built specifically to meet their needs. With the dedicated access and cost-effectiveness they offer, they enhance the user experience for everyone.
Appchain example: Cosmos
There are more than a few ways blockchains implement appchains. For the purposes of this article, we’ll use one of the most prominent examples: Cosmos (ATOM).
Cosmos is a blockchain protocol underpinned by an interconnected “universe” of chains using the Cosmos Software Development Kit and Tendermint consensus mechanism as its bedrock. In Cosmos, appchains are called “zones'' that are connected to the main blockchain, where they can freely communicate with each other as an “internet of blockchains.”
One of the best examples of a Cosmos-native appchain is Osmosis, which serves as the Cosmos Network’s premier decentralized exchange. Osmosis enables Cosmos users to swap tokens and create liquidity pools throughout different zones.
The final word
There’s no question that Web3 is the future of the Internet. It still is. However, more needs to be done to improve the user experience of interacting and transacting on the network, besides making it more accessible and cheaper for the millions and millions of non-crypto natives waiting to be onboarded.
That’s where appchains come in. With their greater customizability, interoperability, scalability, and modularity, they enable Web3 developers greater freedom to build outside general-purpose blockchains where resources can be scarce during peak hours.
With near-instant transactions and low fees, decentralized apps built on dedicated appchains may very well be key unlock and game-changer Web3 needs to attain mass adoption in the coming years.

