On-chain and Economic Impact of Layer 2 (L2) Solutions on Ethereum Network

Key Insights
- L2 solutions like rollups significantly improve Ethereum scalability and reduce transaction costs by processing transactions off-chain and inheriting L1 security.
- The introduction of EIP-4844 and Data Blobs in the Dencun upgrade significantly lowered transaction costs in L2 networks, reducing fees paid to Ethereum and affecting its economic model.
- While L2 solutions positively affect Ethereum's on-chain activity, they pose economic challenges due to reduced fee payments and lower ETH burning rates, contributing to an inflationary supply model.
What is Ethereum
Ethereum is a Layer 1 (L1) blockchain that supports smart contract functionality and enables the deployment of decentralized protocols and applications through the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)—a decentralized virtual environment for executing smart contracts.
After transitioning to the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm in 2022, Ethereum is validated by decentralized nodes that are located worldwide. Nodes verify transactions on the Ethereum network and ensure the blockchain's security.
Anyone can become an Ethereum validator by staking 32 ETH and having the necessary software to run a node. Validators are economically incentivized through rewards in ETH, provided they perform their work honestly. If validators behave dishonestly, they can lose part or all of their staked ETH through a process known as ETH slashing.
One of the key challenges is Ethereum scalability. When network demand increases, gas fees and transaction costs rise sharply, making the network "expensive" to use. Even during non-peak periods, Ethereum's transaction fees remain higher than those of other blockchains such as Solana, BNB Chain, and others.
Another issue for Ethereum is its inability to handle a large number of transactions simultaneously due to the blockchain's technological limitations. Currently, the average Ethereum transactions per second is 13.3, while Solana's TPS is 3,500, TON's is 70, and Sui's is 39.
You can buy ETH on SimpleSwap quickly and with minimal fees. For example, you can exchange ETH for stablecoins or BTC.
Ethereum Scalability: Layer 2 (L2) Technology
Layer 2 blockchains are designed to solve the scalability and high-fee problems of Layer 1 blockchains. L2 networks operate on top of the main network (L1), inheriting its security, while processing transactions off-chain to reduce the load on the main network.
Processed transactions are then approved in the main network and added to the blockchain blocks. Thus, the L1 network is relieved by transferring transaction processing to Layer 2 networks, increasing the overall scalability of the system.
Today, rollups are the most popular solution—L2 blockchains that bundle a large number of transactions into "rollups" and then send them for validation on the L1 network.
The emergence of rollups on Ethereum has partially solved the problem of scalability and high fees, but the impact of L2 on Ethereum is not as straightforward as it might seem. Leading rollups on Ethereum include Base, Arbitrum(ARB), Optimism (OP), Manta (MANTA), and others.
Data Blobs and EIP-4844 for Ethereum
One of the key updates affecting the operation of L2 solutions was the Ethereum Dencun upgrade in March 2024. Part of Dencun was EIP-4844 (Ethereum Improvement Proposal), which introduced a new type of data availability—data blobs.
Data blobs reduce the cost of recording and transferring data from rollups to the main Ethereum network through "blob-carrying" transactions, which create additional space for data in a transaction with a limit of 16 blobs per block.
This significantly reduces the fees associated with L2 solutions for end users because most of the fees are linked to the need to store large amounts of data in the main network via the CALLDATA mechanism. The introduction of data blobs significantly reduces the cost of using L2 solutions compared to the main Ethereum network.
On-Chain Impact of L2 on Ethereum
L2 blockchains play an essential role in the Ethereum ecosystem, contributing to the growth of transactions and active addresses on the blockchain.
Currently, at least two L2 solutions surpass Ethereum in the number of daily active addresses. Base leads with approximately 930,000 active addresses, followed by Arbitrum (447,000), Linea (216,000), and Taiko (129,000).
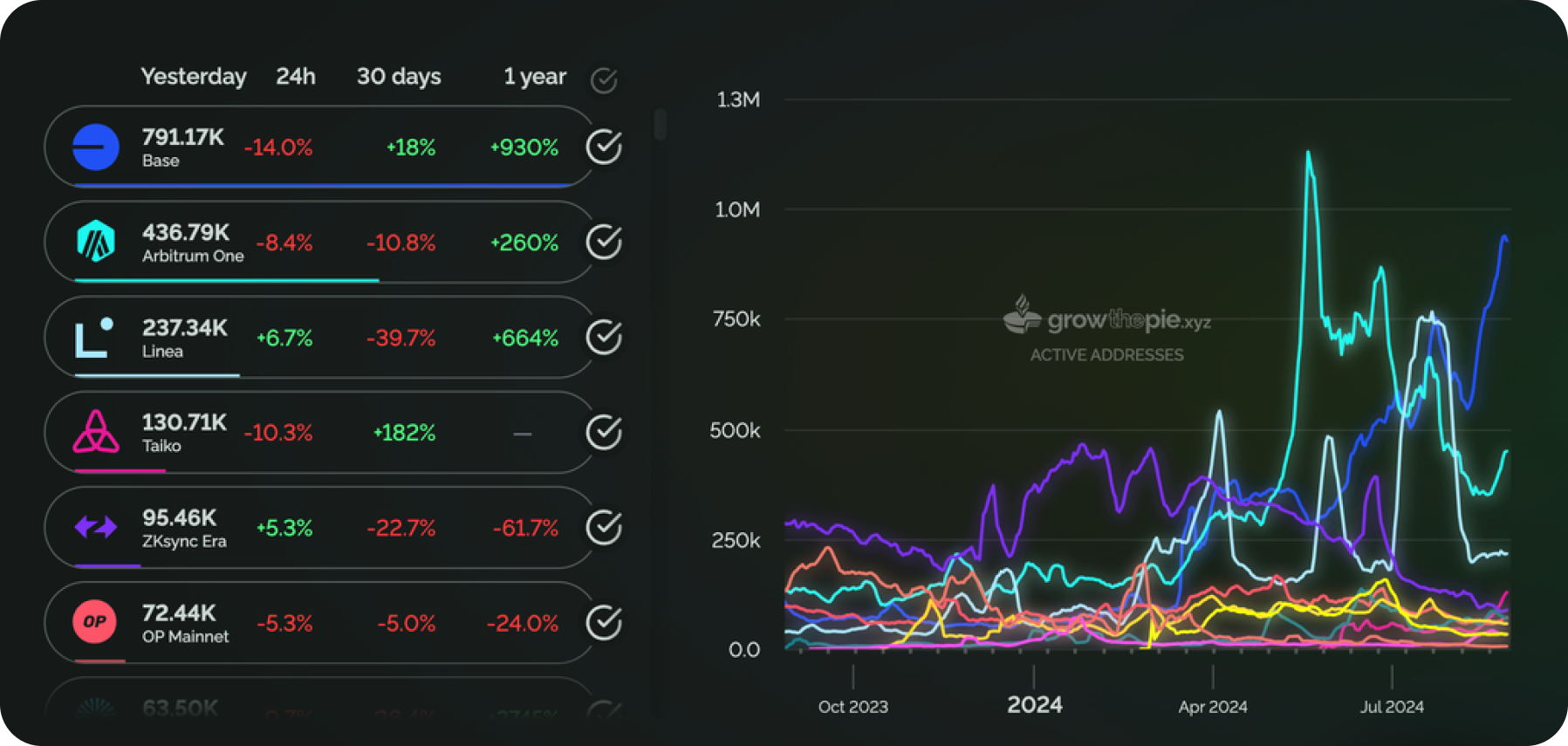
Daily Active Addresses on Ethereum L2 Chains. Source: https://www.growthepie.xyz/fundamentals/daily-active-addresses
In addition to active addresses, at least four L2 solutions surpass Ethereum in daily transactions. Base leads with a significant margin of 4.2 million transactions. Taiko (TAIKO), Arbitrum (ARB), and Manta (MANTA) also surpass Ethereum in this metric.
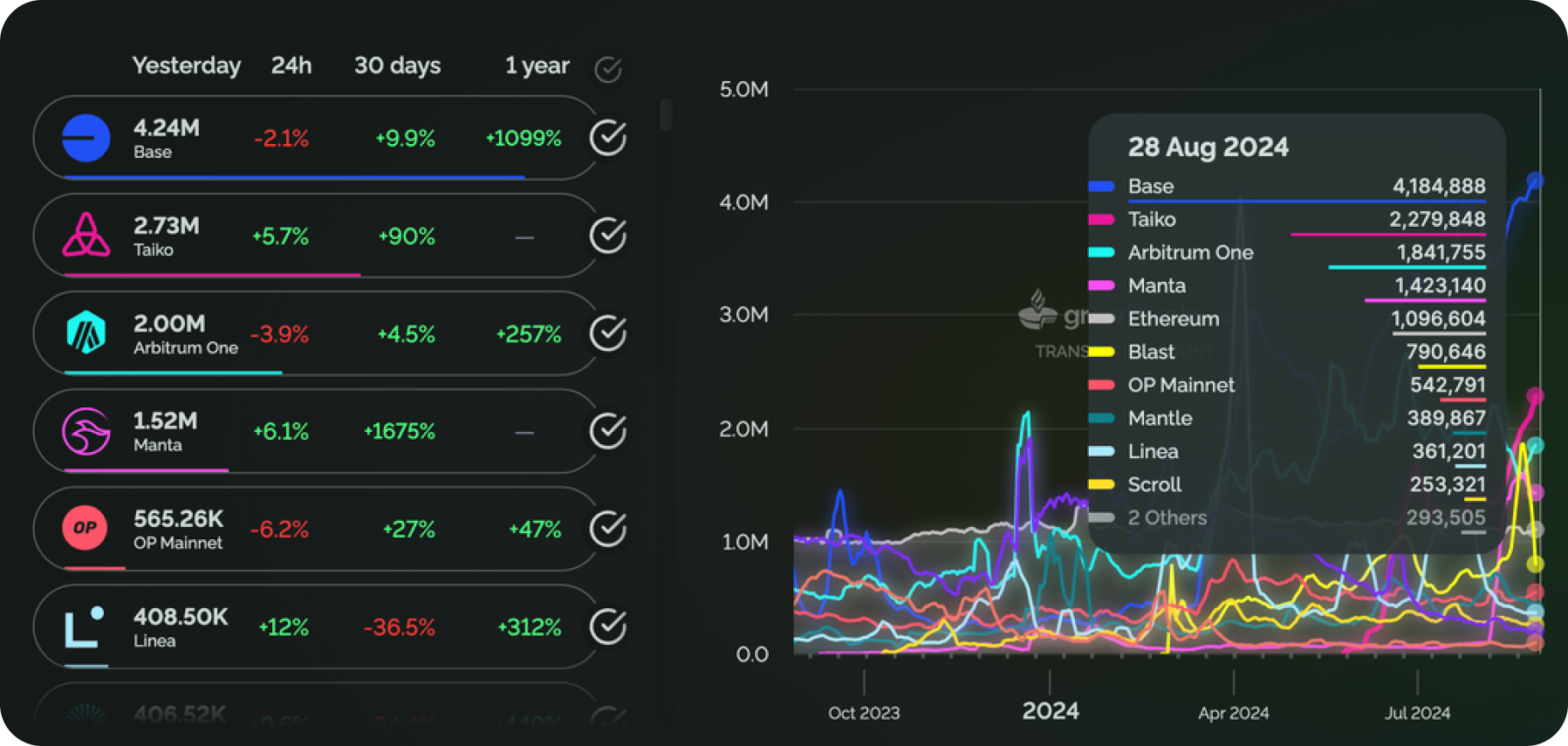
Daily Transactions on Ethereum L2 Chains. Source: https://www.growthepie.xyz/fundamentals/transaction-count
Ethereum also lags behind leading L2 networks in terms of TPS. The current TPS of Ethereum is around 13.3, while the maximum TPS of the Xai rollup is 115. Base's TPS is around 49, Taiko's is 32, and Arbitrum's is 23.
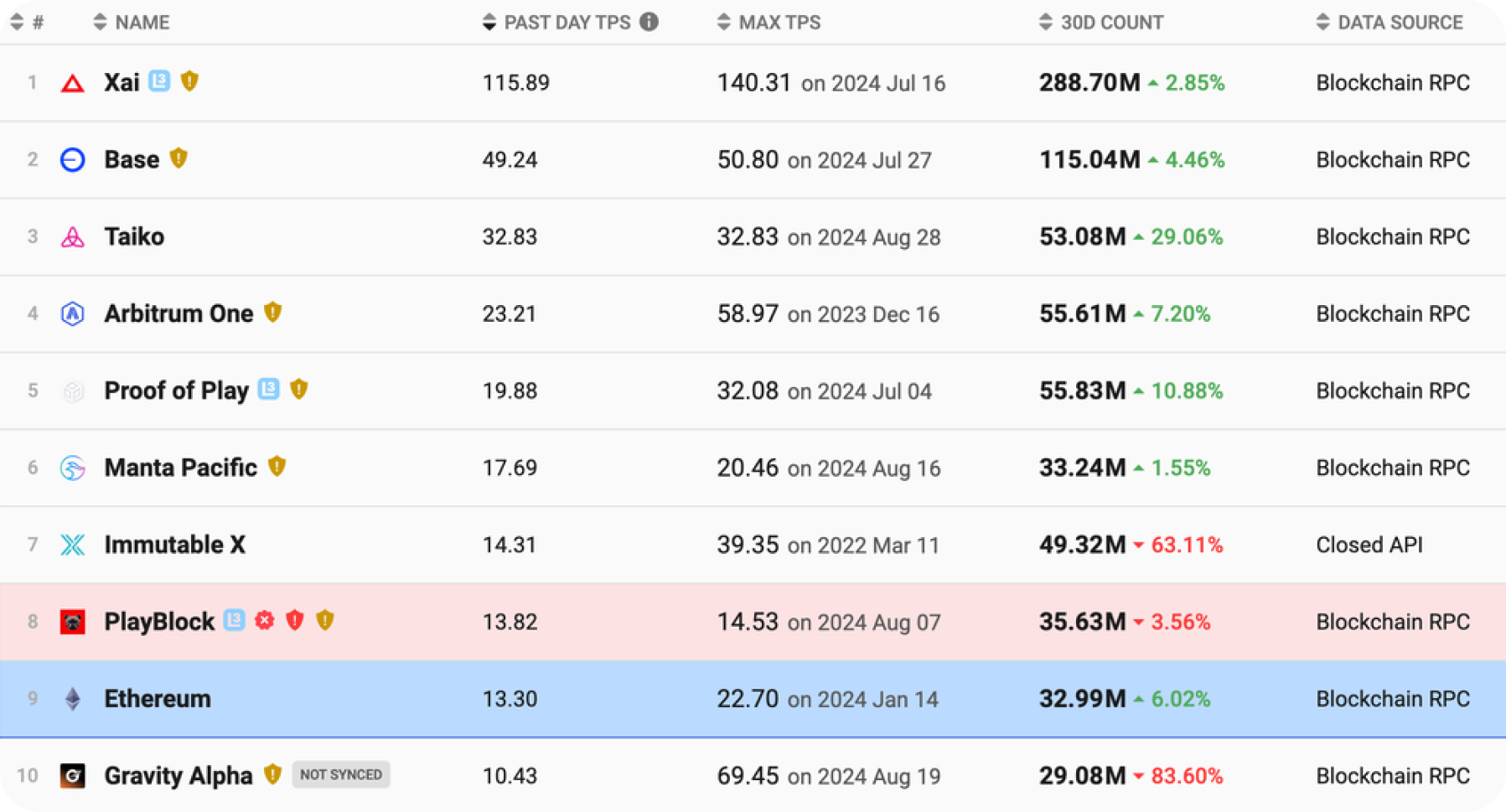
Ethereum vs. L2 TPS. Source: https://l2beat.com/scaling/activity
Thus, L2 solutions effectively address Ethereum's scalability problem by providing additional throughput and offloading the main network. The active use of L2 networks makes them more popular compared to the main Ethereum network, as reflected in the growth of transactions and active addresses.
Economic Impact of L2 Solutions on Ethereum
Although L2 solutions have a positive on-chain impact on Ethereum, their economic impact can be controversial. The introduction of EIP-4844 significantly reduced transaction costs in L2 networks, which is a positive factor for end users and L2 solutions themselves.
However, the reduction in L2 transaction costs leads to less revenue sharing from L2 with Ethereum. Revenue sharing occurs through rent payments—fees for publishing and confirming transaction data on Ethereum, which Layer 2 blockchains pay. Over the past year, the rent paid by leading L2 solutions has decreased by 99%.
This sharp drop occurred after the integration of EIP-4844 and the launch of Data Blobs. As shown in the graph, after the peak values in early March 2024, rent payments sharply declined after March 13, when the Dencun upgrade (and EIP-4844) was implemented.
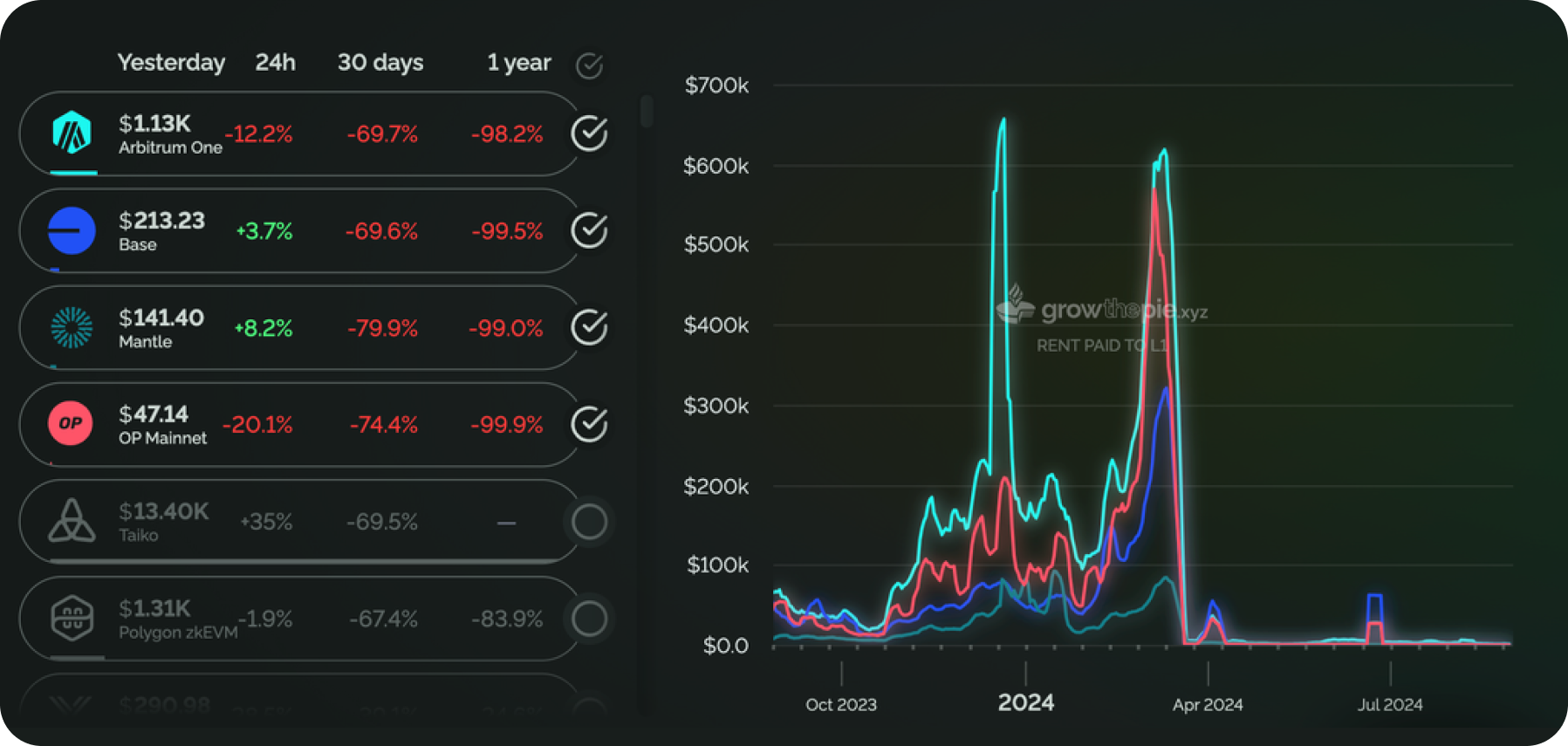
Rent Paid by L2 Networks on Ethereum. Source: https://www.growthepie.xyz/fundamentals/rent-paid
Thus, Ethereum lost some income from L2, while L2 solutions increased their earnings by reducing rent payments.
Another aspect of the economic impact of L2 on Ethereum is the burning of ETH during transactions. L2 solutions were among the leaders in burning ETH, thus contributing to a deflationary model of ETH supply.
However, after reducing fees, L2 solutions have burned significantly less ETH. Currently, no L2 solution is in the top 10 leaders for ETH burning.
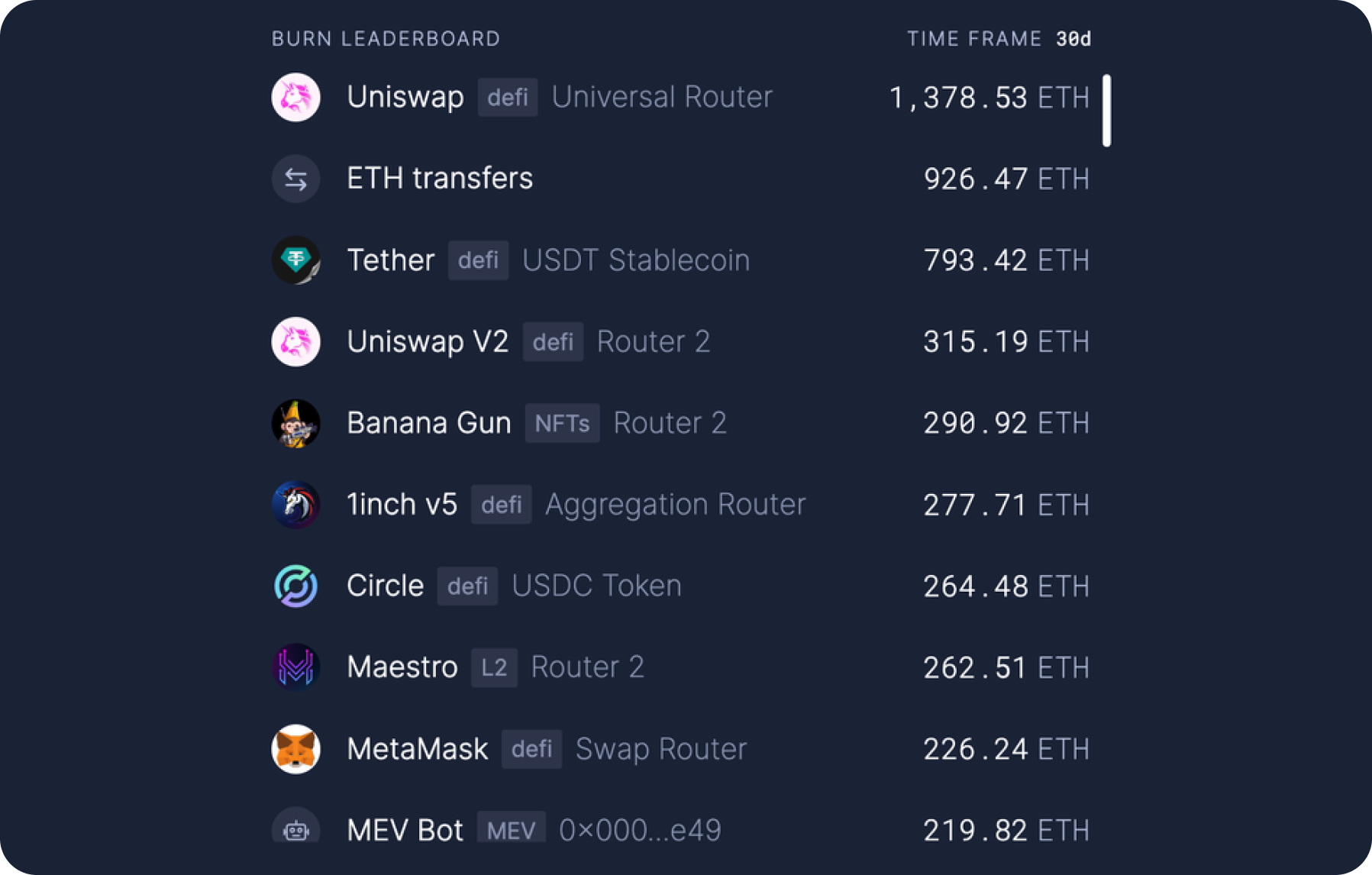
ETH Burn Leaderboard. Source: https://ultrasound.money/
The decrease in ETH burning by L2, along with other factors, has led to ETH supply becoming inflationary, negatively affecting validator earnings and ETH's price outlook.
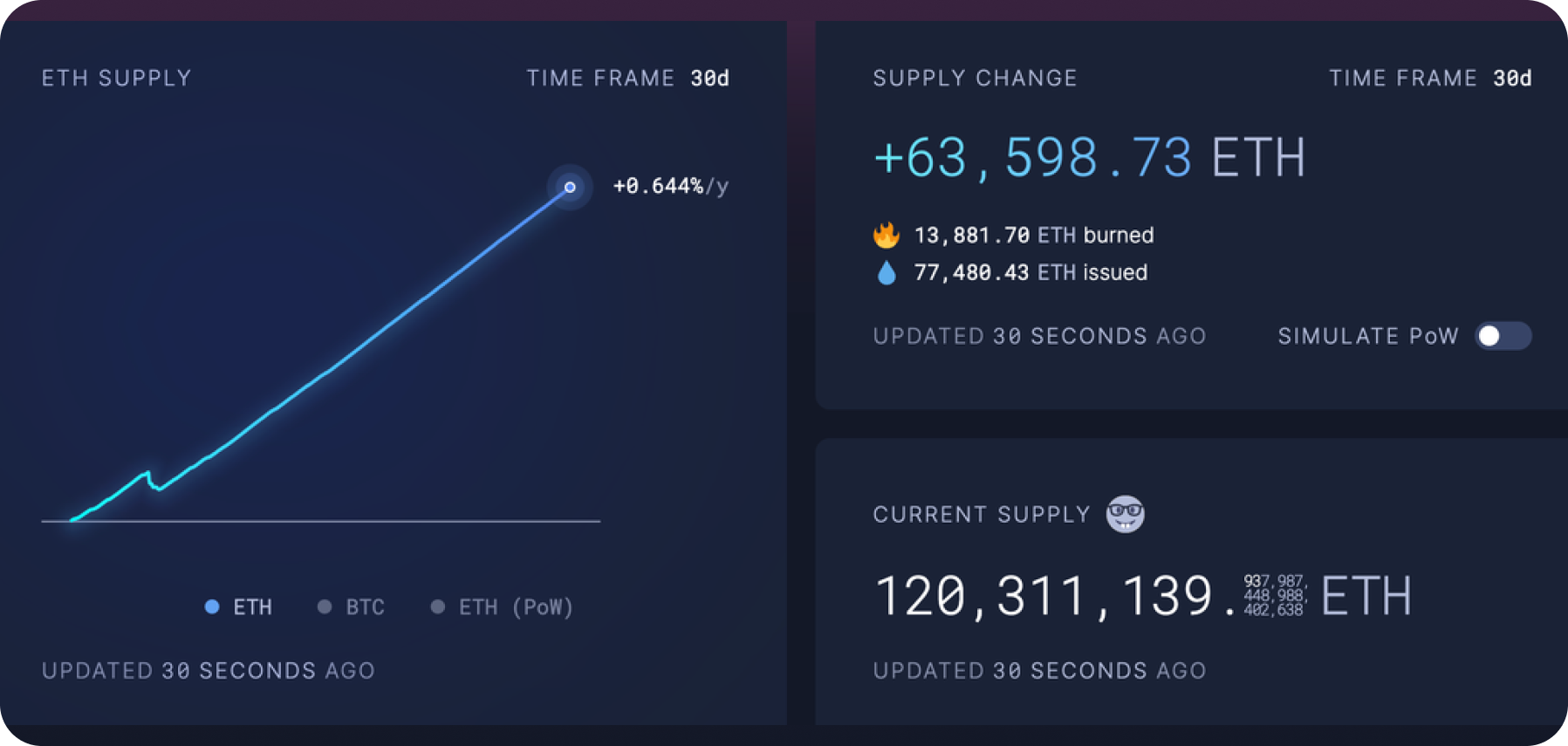
Change in ETH Supply. Source: https://ultrasound.money/
It is worth noting that ETH inflation and the reduction in ETH burning are a result of broader market trends. Currently, user activity has significantly declined due to market uncertainty, which is reflected in the usage of blockchain ecosystems.
Nevertheless, L2 solutions, as one of the leading development directions for Ethereum, undoubtedly play an important role in these processes.
Users can get any cryptocurrency for fiat or crypto on SimpleSwap.
Summary
Layer 2 blockchains are an essential part of the Ethereum ecosystem, solving key issues faced by this Layer 1 blockchain—scalability and transaction costs. By offloading transaction execution to L2, better scalability is achieved, and transaction costs are reduced.
One of the key updates affecting the operation of L2 on Ethereum was the Dencun upgrade and EIP-4844, introducing Data Blobs—a new way of transferring data from L2 networks to the main Ethereum network. Data Blobs significantly reduce the cost of using L2 solutions by lowering fees for data transfer to the L1 blockchain.
L2 solutions have a positive impact on on-chain activity on Ethereum, contributing to the growth of active addresses and daily transactions. Leading L2 solutions already surpass Ethereum in these metrics. L2 solutions also have ahigher TPS than Ethereum, outperforming it several times over. L2 blockchains have become an effective way to address Ethereum's scalability problems and high network fees.
From an economic standpoint, the introduction of EIP-4844 positively impacted L2 solutions and end users. Lowering the cost of sending data to L1 allowed a significant reduction in the economic rent paid by L2 networks to Ethereum. Users also benefit from this update due to the sharp (about 99%) reduction in transaction costs in L2 networks.
The economic model of Ethereum has faced certain challenges due to the Dencun upgrade. The substantial reduction in rent payments by L2 has led to a decrease in Ethereum's overall income.
Additionally, L2 solutions have been burning significantly less ETH, affecting its supply model, which under current market conditions has become inflationary.
The information in this article is not a piece of financial advice or any other advice of any kind. The reader should be aware of the risks involved in trading cryptocurrencies and make their own informed decisions. SimpleSwap is not responsible for any losses incurred due to such risks. For details, please see our Terms of Service.


