Explainable AI Explained
This blog post will cover:
- Solution for AI issues
- How XAI works
- XAI use cases
- Imperfections of XAI
- Conclusion
Over the past months, several well-known tech gurus, such as Bill Gates and Elon Musk, have voiced their concerns about the dangers of the AI revolution. Although artificial intelligence has been around for quite some time, this was largely in simple forms.
Now, AI has developed significantly. Neural networks are working more smoothly, chat bots can answer almost any question and offer a solution for a number of tasks. However, there are still some problems the current AI faces. The spread of artificial intelligence tech requires help, and this help has come from XAI. Today we will see what it is and how it actually works.
Solution for AI issues
True artificial intelligence is a much-more recent technology and is currently based on neural networks and machine learning. It all started when dotcom companies wanted to figure out the personal preferences of their users. Ad companies wanted to know which ads to show to which users to maximize profit. Google aimed to come up with the best online search results based on each individual. Online entertainers like YouTube or Netflix desired to show you content that you would most likely enjoy. Machine learning algorithms were first widely used in these applications.
However, the problem with machine learning is that while it can work pretty well, no one, not even the experts developing the software, know exactly how it generates the output. This means that AI can produce outputs that cannot be unambiguously explained based on the instructions it received. This might not be a problem as long as you use AI for entertainment, after all the worst thing that could happen is a bad or weird movie suggestion.
Yet once you start using real AI technology in self-driving cars, financial services, government administration, law enforcement and even military technology, the concerns get much bigger. The solution is explainable AI or “XAI” which enables experts and users to comprehend why the AI is doing what it is doing.
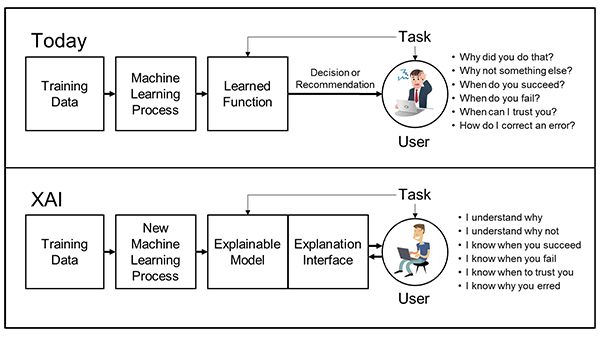
For a clearer understanding, take a glance at the DARPA’s schematic picture explaining the difference between two technologies, AI and XAI:
How XAI works
XAI is important not only because of serious safety concerns. Unless the developers can understand everything their program is doing, they cannot be sure that it will always be 100% successful on correctly executing the tasks it was assigned to do. This becomes a huge problem for scientific, IT and big-data applications, where it is not obvious to anyone whether the output is correct or not.
XAI is a set of principles and tools to help developers understand the software they are working on. These principles are a little bit similar to ISO quality assurance guidelines. For example, explainable AI offers development tools that help visualize and understand different outputs of the ML (machine learning) algorithm based on different inputs. This can greatly help developers in understanding the results of their own ML algorithm.
Apart from help with visualization and data interpretation, XAI also comes with a number of development principles, meaning that the software developers are limited not to develop an AI further, until they can adequately understand it, even if it already generates seemingly good results.
XAI use cases
Now when we know how XAI works, there’s another question raised: where explainable AI could be used? Are there any real use cases for this tech? Let’s take a look at a list of sectors, where XAI might be helpful.
- MedicineIn the field of healthcare, the incorporation of explainable AI systems plays a crucial role in assisting doctors with patient diagnoses. This integration fosters a sense of trust between medical professionals and the AI system, as doctors gain insights into the reasoning and methodology behind the system's diagnostic outcomes.
- FinanceThe financial sector utilizes XAI to assess and determine the approval or rejection of various financial claims, including loan applications and mortgages. Additionally, XAI aids in identifying instances of financial fraud, enhancing the overall security and reliability of financial processes.
- Autonomous machinesIn the realm of autonomous vehicles, the implementation of XAI becomes instrumental in elucidating driving-related choices, particularly those pertaining to safety. By providing passengers with a clear understanding of how and why the vehicle makes specific driving decisions, they can experience a heightened sense of security. Consequently, passengers become more aware of the vehicle's capabilities and limitations in handling various driving scenarios.
- MilitaryWithin the military domain, the adoption of AI-based systems necessitates the incorporation of explainability. This measure ensures that service personnel can develop trust in the AI-enabled equipment they rely on for their safety. By comprehending how these systems arrive at their decisions, military personnel can establish a higher level of confidence and reliance.
Imperfections of XAI
All this aims to minimize the so-called “black box” phenomenon (we mentioned it here earlier). This refers to the fact that by playing with certain parameters you can make an ML (machine learning) algorithm generate the desired output from the input, without actually understanding how it is doing it. But since XAI is not an exact technology, but rather a way of doing things, once it comes to complex technology that is beyond the limit of immediate obvious human expert comprehension, there will always be an uncertainty factor.
Just like in some cases we might never be completely sure whether a ML based AI is 100% doing what it should be doing, sometimes we can also not know for sure if our XAI approach was a 100% successful or not. The thing that many experts are starting to point out is that the ability of any technology to perform complex tasks and the control and understanding we have over said technology seems to be inversely correlated.
Conclusion
It is likely that the more advanced AI becomes, the less we will know what exactly is happening inside the program and the less it will be in control. This problem might never be solved, but XAI can help to at least keep the risks manageable.
The development of explainable AI might help companies and whole industries work well and prevent (or minimize) the number of failures and bugs within any ecosystem using artificial intelligence. Considering the speed of AI growth nowadays, we might expect the increase of use cases when big firms integrate AI into their work systems. Explainable AI, in turn, will be aimed to manage the work of neural networks and keep it clean.
Want to read more about artificial intelligence? Here are some of our previous articles: The Role of AI in the Finance Industry, We Asked AI’s “Opinion” About Crypto and AI Took Over SimpleSwap Twitter Account.