Filecoin Fundamental Analysis
Key Insights
- A deep look into Filecoin network’s features, instruments, protocols, structure, team, and risks.
- Filecoin’s key features prevent possible attacks and allow for safety and data integrity in a decentralized network.
- Filecoin’s economic model provides possibility to create a sustainable ecosystem where participants are rewarded for their efforts in making the network work.
The Filecoin project was introduced in 2017 by founders Juan Benet and Professor David White.
What Is Filecoin
The story of the Filecoin project began with the realization of the need for an efficient and secure storage system in a decentralized environment. The founders sought to address the problems associated with centralised data stores, such as limited scalability and vulnerability to attack.
The initial distribution of FIL tokens occurred through an ICO (Initial Coin Offering) in 2017, where tokens were put up for sale to raise investment for the development of the project. Then, in 2020, the Filecoin core network protocol was launched, giving network participants the opportunity to earn FIL tokens for providing storage and processing space for files.
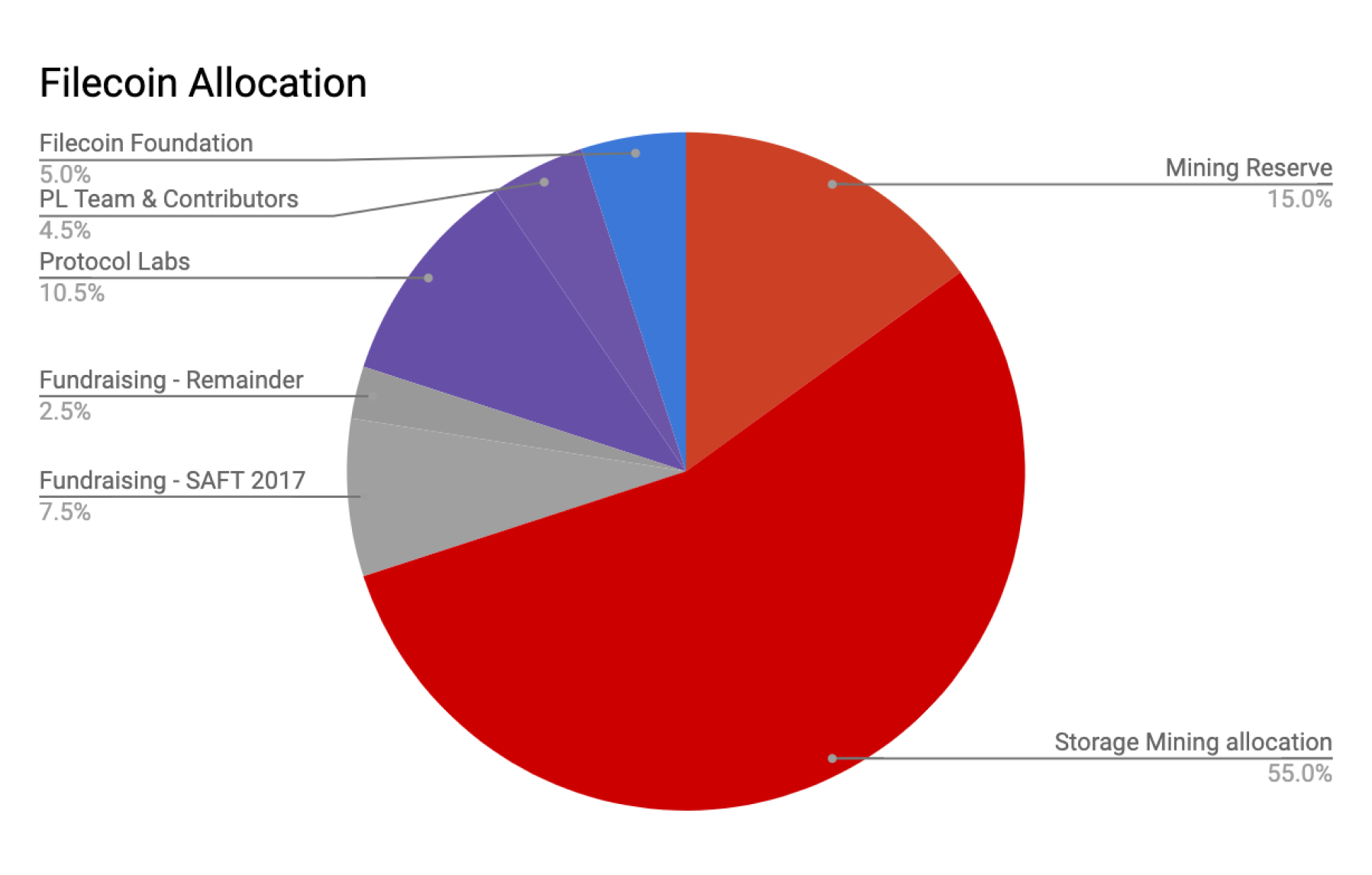
The goal of the Filecoin project is to create a decentralized file storage network where users can safely and efficiently store their data, and be rewarded for the storage provided.
Filecoin's mission is to provide a decentralized and secure data repository where users are in control of their files and information, without having to trust centralised organisations.
Users can get FIL on SimpleSwap.
FILE CoinMarketCap Rating
Market cap: 23rd place ($4.17B)
Volume (24h): 17th place ($413.22M)
Total supply: 1,960,870,030 FIL
Competitive Environment Analysis
Filecoin faces a number of key projects in the decentralized storage space, each with its own characteristics:
- IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
This protocol and network is designed to store and share files in a decentralized environment, similar to Filecoin. Unlike Filecoin, IPFS focuses on the protocol and has no inbuilt reward system for providing storage.
- Sia
Another decentralized storage network that offers similar features to Filecoin. Sia also uses blockchain technology to ensure data security.
- Storj
This is a decentralized data storage platform offering solutions for developers and enterprises. Unlike Filecoin, Storj uses a pay-per-use storage model.
- Arweave
It is a blockchain platform for long-term data storage using the concept of "persistent memory". It focuses on secure long-term data storage.
In addition, centralised cloud platforms should also be considered:
- Google Cloud Platform
Google provides cloud storage through Google Cloud, providing a wide range of storage and processing services.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon also provides cloud storage services through AWS, including various storage services such as Amazon S3 and Amazon EBS.
Filecoin promises efficient and secure platform that attracts the interest of users and developers. However, it will have to overcome challenges in scaling and attracting more participants to successfully compete in the market.
Filecoin Technology
Filecoin technology includes a number of key aspects that cover technical specifications and innovations.
Proof of Replication (PoRep)
is a mechanism in the Filecoin network that ensures that the repository actually keeps a copy of the data, rather than just referencing it. It prevents possible attacks, such as submitting false evidence of storage, and ensures data integrity in a decentralized network.
The PoRep workflow includes the following steps
- Initialisation
The storage receives the data from the client and allocates a specific location for it.
- Sealing
The data in the sector is sealed, which means that it is encrypted and protected. This process also generates a proof that the data is actually stored.
- Replication Proof Generation
Using cryptographic techniques, the repository creates a proof that confirms that it has replicated the data exactly as promised.
- Proof Compression
The resulting proof is compressed to reduce the amount of data transferred. This helps to optimise resource usage and improve performance.
- Sending to the network
The compressed proof is sent to the Filecoin network for verification. If the validation is successful, the vault receives an acknowledgement of its operation.
PoS & PoW VS PoSt
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
PoS is based on the idea that the more coins an owner has, the more power they have in the system.
In PoS, new blocks are created by participants who have a stake in the cryptocurrency. The choice of the block creator is based on a random or pseudo-random selection that depends on the size of their stake.
The main idea is to incentivise participants in the network to act honestly, as they risk losing their funds in case of unscrupulous behaviour.
- Proof of Work (PoW)
PoW requires network participants to perform some computational work to create new blocks and validate transactions.
Network participants solve complex mathematical problems, and the first person to solve the problem gets the right to create a new block and be rewarded for their work.
PoW secures the network by expending a large amount of computing power required to do the work, making data manipulation difficult and not beneficial. Thus, PoRep provides proof that the vault is actually storing a copy of the data, making it essential to the safety and security of file storage on the Filecoin network.
Proof-of-Spacetime (PoSt)
It is a mechanism in the Filecoin network designed to confirm that a storage node is still storing data for a certain period of time. This mechanism ensures the long-term security and availability of data on the network.
When a storage has already proven that it has copied a copy of the data it has agreed to work with, PoSt requires the continuation of the proof of the following:
Data Storage: The repository must continue to store the requested data.
Data Availability: The data must be available for retrieval at any time.
Data Sealing: The data must remain sealed, that is, protected from alteration or corruption.
PoSt in Filecoin is implemented using two main sub-methods:
- WinningPoSt
Used to prove that a storage node has a replica of the data at a specific time that has been requested, and is used in the consensus process to create blocks.
- WindowPoSt
It is used to prove that the storage node maintains a data replica continuously over time. It is used to verify node activity and maintain long-term data integrity.
Both of these PoSt sub-methods are important to ensure the long-term reliability and resilience of data storage on the Filecoin network.
Filecoin Smart Contracts
Smart Contracts in Filecoin is a mechanism that allows users to create and deploy software agreements on the Filecoin blockchain.
These agreements are executed automatically under certain conditions set in their code, without the need to trust a third party. Below are some key aspects of Filecoin's smart contract technology.
- Programmability
Smart contracts in Filecoin can be written in a variety of programming languages and contain logic that defines the conditions and actions to be performed.
- Automatic Execution
When the conditions specified in a smart contract are met, the contract automatically executes the appropriate actions. This reduces the risk of human error and ensures reliable execution of agreements.
- Decentralization and security
Smart contracts in Filecoin are executed on a blockchain network, which ensures they are censorship-resistant and protected from manipulation.
Examples of smart contracts in Filecoin include:
- Data Warehouse Management
Contracts can automatically manage data storage on the Filecoin network, including extending retention periods and storage selection.
- Data Access Management
Contracts can manage access to data and set access rights for different users.
Filecoin's smart contract technology opens up a wide range of opportunities for developing dApps and provides transparency, reliability and security.
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
IPFS is a protocol and network for the distributed storage and sharing of files on the Internet.
Instead of files being addressed by location, as is the case in traditional networks, in IPFS files are addressed by content identifiers called hashes. This allows users to share data without depending on centralised servers.
IPFS Main Features
- Content-based hashing
Files in IPFS are addressed with hashes that are based on their contents rather than their location. This makes it possible to uniquely identify files and ensures their availability on the network.
- Distributed Storage
Files in IPFS are distributed across nodes in the network, providing fault tolerance and improved performance. Each node in the network can store a copy of the files, making data available regardless of the state of individual nodes.
- Caching and top-down networking
IPFS automatically caches popular files, which improves access speed. It also supports the concept of top-down networking, allowing users to connect to data through any available nodes.
- Open protocol
IPFS is an open protocol, which means that its specifications are available to everyone and anyone can connect to it. This fosters an ecosystem and improves the functionality of the network.
IPFS is widely used for a variety of purposes, including file storage and sharing, decentralized application development, digital asset creation, and more. It represents an important component of a decentralized internet infrastructure that provides transparency, security and resilience to censorship.
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) and Filecoin are two related projects developed by the Protocol Labs team, and they have a number of important connections.
- Data storage
IPFS provides a protocol and facilities for distributed file storage and sharing. Filecoin, on the other hand, provides a reward mechanism for storing this data. Nodes connected to the Filecoin network can provide free storage space for IPFS files and receive payment in the cryptocurrency FIL for the services provided.
- Incentives to participate
Filecoin provides economic incentives to participate in the network and offers rewards for storing and transferring data. This enhances and strengthens the IPFS network as nodes are motivated to provide available space for file storage.
- Compatibility
IPFS and Filecoin are tightly integrated with each other. Files that are stored in IPFS can be rented and stored on devices connected to the Filecoin network. This provides an additional layer of security and reliability as data is duplicated and stored on multiple nodes in the network
- Decentralized data management
Together, IPFS and Filecoin provide decentralized data storage and management. This means that files can be accessed and stored even when centralised servers are down, increasing the resilience and reliability of the entire system.
In this way, IPFS and Filecoin together form a powerful infrastructure for decentralized file storage and sharing, providing resilience and transparency in the network.
Filecoin Project Team
Filecoin is a large community of talented and dedicated professionals who are actively involved in various aspects of developing, maintaining and promoting the protocol. Some of the key individuals and teams associated with the project include the following.
- Filecoin Foundation
A non-profit organization that aims to support and grow the Filecoin ecosystem. It funds projects to improve the protocol, supports developers, organizes events and research, and encourages the adoption of Filecoin in various areas including data storage and dApps.
- Alex Feerst
CEO of the Murmuration Labs project. Previously served as legal advisor to Protocol Labs and Chef Robotics, and as founder's advisor to the Digital Trust and Safety Partnership.
- Joseph Lubin
Founder and CEO of ConsenSys and co-founder of the Ethereum Project.
- Sandra Ro
CEO of the Global Blockchain Business Council.
- Protocol Labs
The company behind the development and support of Filecoin. It consists of developers, researchers, and engineers working on various aspects of the project including protocol development, network enhancements, security, marketing and more.
Filecoin Economic Model
Below is the evaluation of token distribution mechanisms, economic incentive and inflation models.
Filecoin's economic model study includes evaluation of token distribution mechanisms, economic incentive and inflation models. Let's look at each of these aspects:
- Token distribution mechanisms
Filecoin started its journey with an ICO (Initial Coin Offering) in 2017, where investors could purchase FIL tokens in exchange for ETH or other cryptocurrencies. This phase allowed for the initial distribution of tokens to community members. In addition, tokens were also distributed to the development team, investors, and partners.
- Economic incentive models
Filecoin uses an economic incentive model based on rewards for storing data and performing various tasks on the network. Participants who provide data storage and engage in proof of space and time are rewarded in FIL tokens. This incentivises participation in the network and provides decentralized storage.
- Inflation
Filecoin's economic model includes an inflationary mechanism that regulates the issuance of new tokens into circulation. Inflation in Filecoin is related to the supply and demand for data storage on the network. If demand for data storage exceeds supply, inflation can be increased to incentivize additional supply of storage. Conversely, if supply exceeds demand, inflation can be reduced.
Filecoin's economic model is designed to provide an incentivised environment for data storage and network security. The token distribution mechanisms, economic incentive and inflation models work in concert to create a sustainable ecosystem where participants are rewarded for their efforts in making the network work.
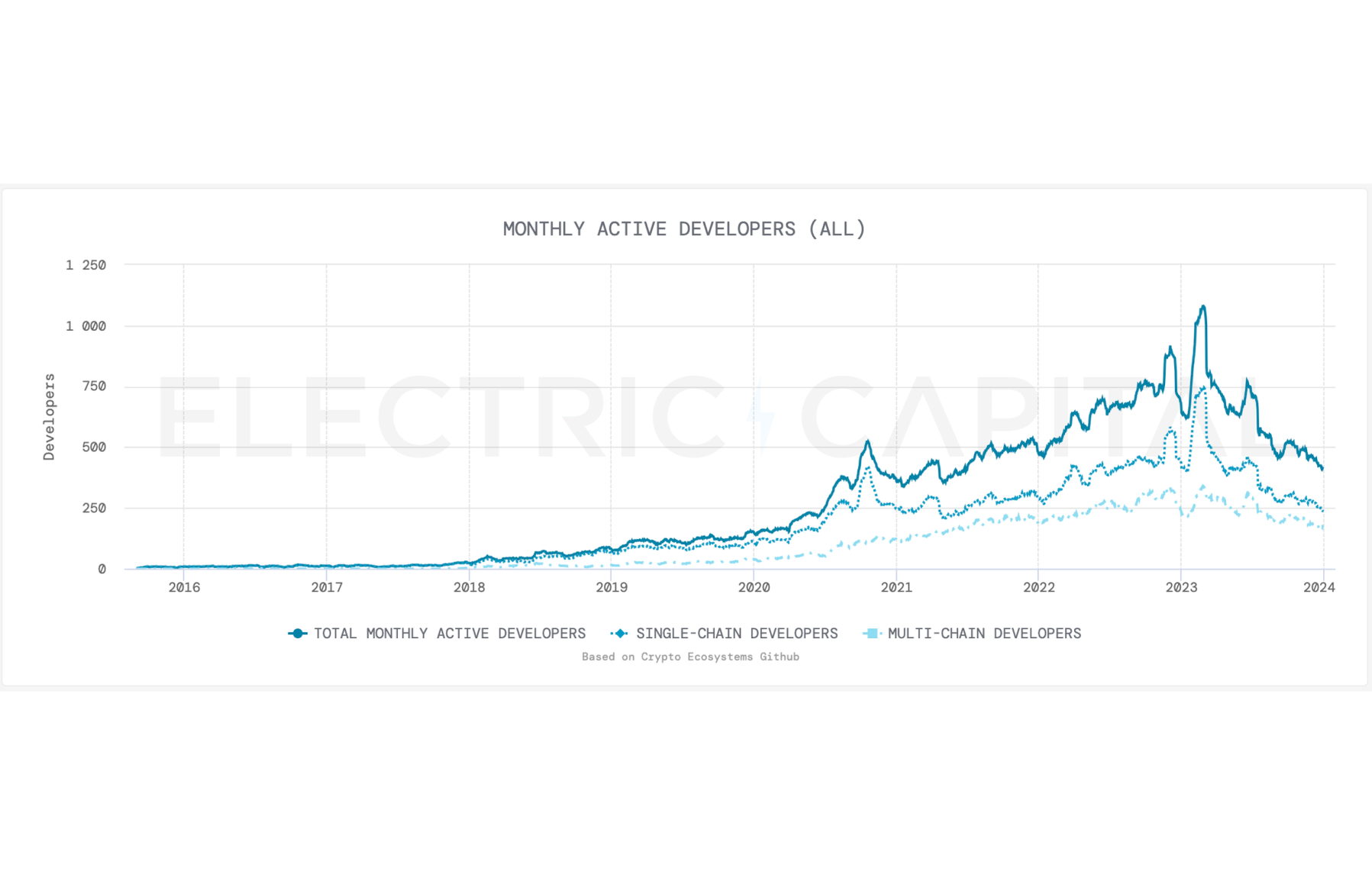
Filecoin Development Metrics
According to Electric Capital Developer Report, the activity of developers on the Filecoin network corresponds to the growth of the cryptocurrency market.
The Daily Active Deal PiB Statistics show daily transaction activity in petabytes (PiB) on the Filecoin network.
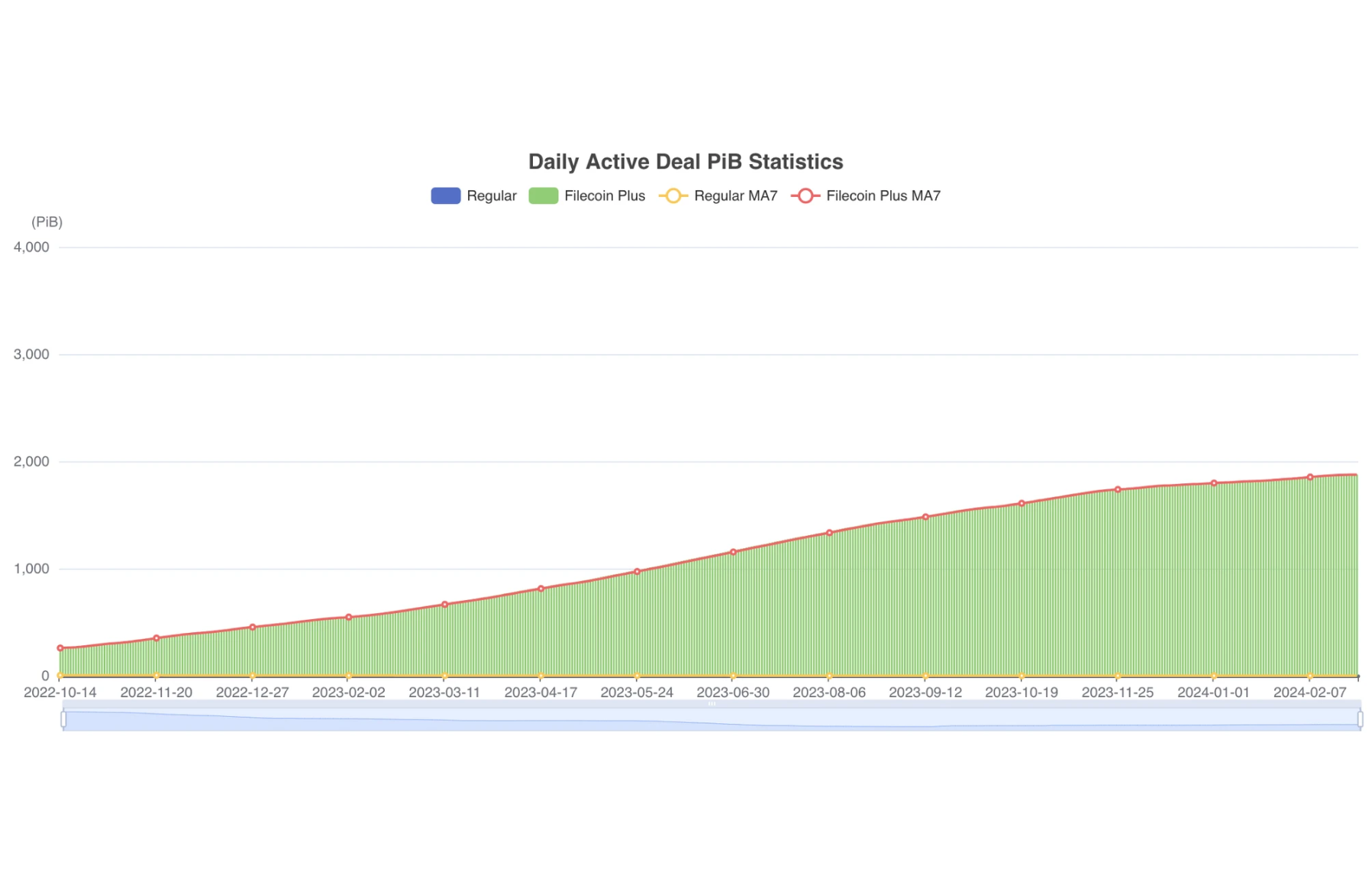
This metric is an indicator of Filecoin network utilisation, which reflects the amount of data stored and transferred through the network during each day. The strong growth of this metric indicates an increase in user activity and acceptance of Filecoin as a platform for storing and sharing data.
The FIL project has its own Telegram channel with over 3,500 participants.
The X platform has 673.1 thousand subscribers.
Filecoin Risks
A risk assessment of the FIL token (Filecoin) may include several aspects.
- Technology risk
The development of Filecoin's technology and the successful implementation of its roadmap may affect its value and attractiveness to users and investors. Technical issues such as security vulnerabilities or performance flaws could affect the project's credibility and its ability to realise its goals.
- Market Risk
The price of the FIL token may be subject to cryptocurrency market volatility and external economic factors. This may create risk for investors and users who may lose some or all of their investment as a result of changes in the price.
- Competitive risk
Filecoin operates in a competitive environment with other projects offering similar storage and transfer services. Developing competitive solutions and attracting users may present challenges and the need to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Regulatory risk
Changes in the regulatory environment, including legislation on cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, may impact Filecoin and its users. Negative regulatory measures could hinder the project's operations or even lead to its closure.
- Technical risk
Like any blockchain project, Filecoin is subject to technical problems such as hardware failures, network attacks or software bugs. Such events can temporarily interrupt the network and affect its reputation.
Summary
Based on the analysis of the reviewed Filecoin project data, its important contribution to the development of decentralized data storage and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem becomes evident. Despite the identified risks associated with technological, market and regulatory aspects, Filecoin continues to attract attention from users and developers.
Active participation of the developer community, stable growth of data volumes transmitted through the network testify to the significance and sustainability of the project.
Thus, the Filecoin project remains an important player in the crypto market and decentralized technologies, demonstrating its ability to adapt to changing conditions and attract new participants due to its innovative nature and sustainability.
Users can exchange all cryptocurrencies mentioned in this article for fiat or crypto on SimpleSwap.
The information in this article is not a piece of financial advice or any other advice of any kind. The reader should be aware of the risks involved in trading cryptocurrencies and make their own informed decisions. SimpleSwap is not responsible for any losses incurred due to such risks. For details, please see our Terms of Service.


